On the verge of 5G massive deployment, Mobile Operators are under intense pressure to roll-out the new 5G networks. For operators that prepare their mobile networks to support new 5G services, there is currently a limited choice of vendors to choose from. Therefore, to be able to deliver advanced 5G services, operators need to change their mindset to be able to adopt radical approaches, accelerate innovations, and overcome vendor lock-in.
After several years of vendor consolidation, the industry has been left with a minimal number of dominant giants in the telecom system vendor space. Furthermore, geo-political tensions, such as the US ban on Chinese vendors, have increased vendor dependencies, and have limited the number of available vendors. Operators will, therefore, need to globally focus on a re-development of a healthy 5G vendor environment to support their infrastructure needs.
5G Disaggregation and Cloudification
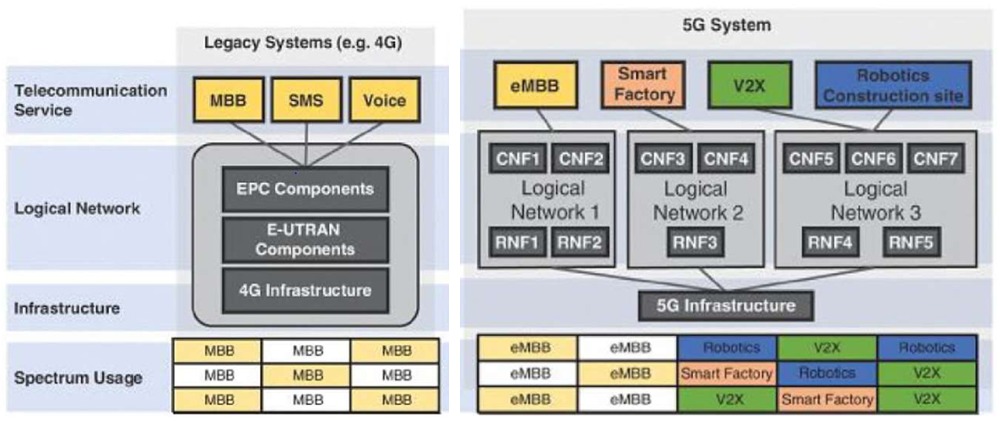
The way forward for 5G operators is an open 5G ecosystem with core disaggregation and cloudification. This means moving from existing monolithic systems to a more modular and flexible approach with open interfaces and APIs. In the existing systems, architecture hardware and software are tightly coupled and usually provided by the same supplier. However, moving to open-source architecture, the telecom industry may achieve significant savings due to scalable designs, automation, and high efficiency.
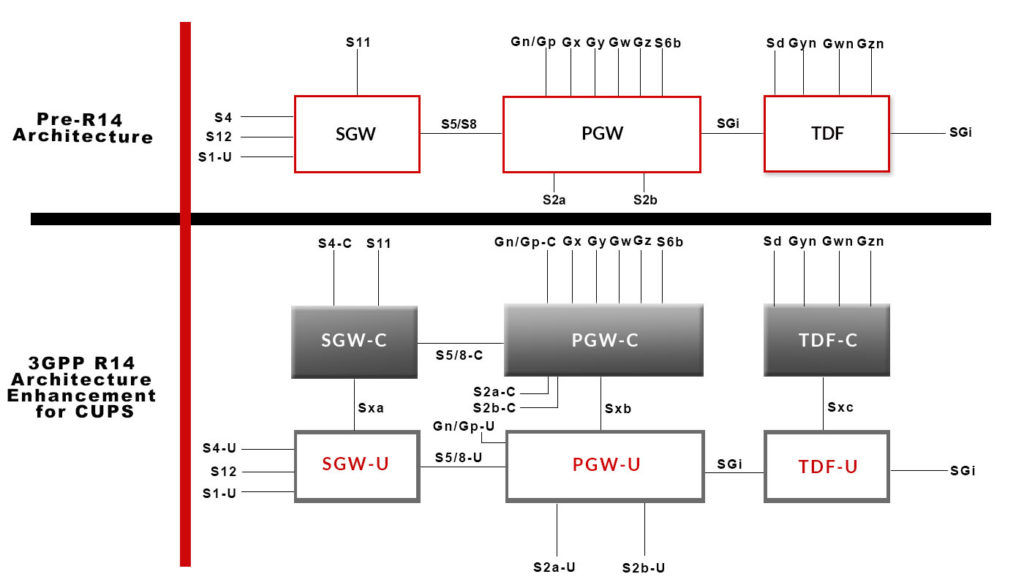
The challenge for every Operator will be to support a multi-vendor RAN environment with an open ecosystem. A cloud-native solution will support control and user plane separation (CUPS) architecture. Disaggregation and decoupling hardware from software may assist moving cloud technology to the edge and help provide advanced network scalability.
With the upcoming advanced 5G services, there is an expected explosion in the number of applications and the corresponding 5G edge sites to support those numbers from a network point of view. It is estimated that new 5G services demands and the new millimeter-wave frequencies to be used will lead to network densification and a considerable increase in the number of sites per Operator.
The agile 5G Telco
Smart ways and unified platforms are one way to cater for this. Core disaggregation and cloudification can create a common platform to handle 5G, MEC, and enterprise applications simultaneously. A common NFV infrastructure may support a Telco cloud model, which is ideal for enterprise 5G apps. This will increase visibility across the entire infrastructure and simplify decision making. Furthermore, automation will improve agility across this cloud environment.
Disaggregation and the cloud are the foundation for agile telcos and service providers. The ultimate goal would be to support any hardware and any app with any cloud, whether it is a public, private, or a telco hybrid cloud network. For successful 5G networks, Operators need to evolve the core to the cloud, push software cloud to the edge, and optimize radio with more spectrum and advanced propagation techniques.
Compared to LTE technology, ten times more control areas are expected to be present with 5G. New demanding verticals, such as public, enterprise, industrial, private clouds, will dynamically be competing for optimal connectivity. Radio disaggregation will help in this direction by being able to observe, predict, and control the upcoming networks. Furthermore, it is estimated that a 5G system using Open and Disaggregated radio, will require around 20-30% less overall investment on CapEx and OpEx.
Open RAN
5G operators are currently investigating the benefits of OpenRAN. An OpenRAN system with open standards will limit the dependence on specific vendors and reduce the frustration around the ability to change their network infrastructure. An OpenRAN system may offer a significant TCO reduction. The possibility to run multi-vendor RAN applications will avoid vendor lock-in and make possible a fast vendor change in case it is needed. This will enable operators to run multiple applications on the DU and avoid proprietary software/hardware, thus, minimizing RAN inventory and lowering the maintenance and support costs.
Operators are starting now to make known their intentions towards pushing vendors to open interfaces. It seems that vendors are reluctant to proceed for apparent reasons. They would rather be the ones to supply end-to-end equipment hardware and software with proprietary interfaces when needed. Furthermore, the lack of a low-cost RRU, which could be feasible in an open-source and centralized environment, is usually a significant obstacle for C-RAN and 5G deployment. However, most operators would definitely consider deploying RRUs and BBUs from different vendors in an OpenRAN fashion, which would offer extra flexibility and cost savings. Doing so would also allow a potential vendor swap, especially since we are entering in an unstable vendor environment with political decisions that may overshadow technical or commercial agreements. From the Operators’ point of view, 5G disaggregation and OpenRAN will transform the telecom industry and pave the path towards a flexible, scalable, and automated 5G ecosystem.