Introduction
In order to enable the UE to save battery, it is very important that the UE can switch off its receiver (and transmitter) when there is no data to be transmitted or expected for that UE. This makes it possible to achieve a significantly longer standby time in the UE compared to “talk” (or active) time. At the same time, the UE should be reachable by the network (e.g. via paging) and, if it wants to transmit data, it should quickly be able to access the system.
One of the important control plane topics of 5G is the mobility framework, which consists of the state machine design for the Radio Access Network (RAN). State machine design for 5G RAN is challenging due to the high number of 5G use cases, which have divergent and sometimes contradictory requirements. For example, there are more than 50 use cases identified for 5G in the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP).
State Model For The 5G Access
A novel state model is proposed for the 5G Access enabling an efficient UE sleeping, a fast and lightweight transition from sleeping to active states, and joint access optimizations. The model consists of three states: RRC_IDLE, RRC_CONNECTED, and RRC_CONNECTED_INACTIVE.
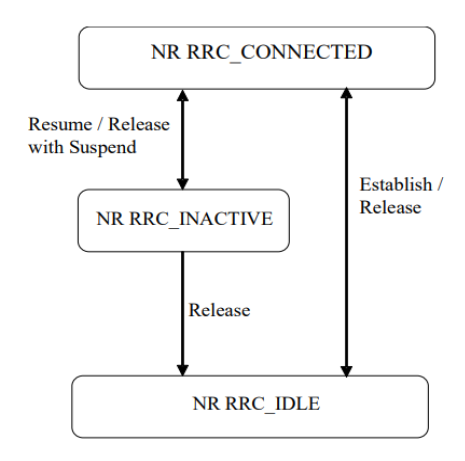
State model for the 5G architecture (only RAN states)
In the novel model, the state transitions from RRC_IDLE -> RRC_CONNECTED are expected to occur mainly during the first initial access (e.g. when the UE attaches to the network) or as a fallback case (e.g. when the devices and/or network cannot use the previously stored RAN context). As a consequence, this transition is not expected to occur as often as in LTE.
On the other hand, transitions from RRC CONNECTED INACTIVE -> RRC CONNECTED are expected to occur quite often and should be optimized as a lightweight and fast transition.
UE states and state transitions
A UE is either in the RRC_CONNECTED state or in the RRC_INACTIVE state when an RRC connection has been established. If this is not the case, i.e. no RRC connection is established, the UE is in RRC_IDLE state. The RRC states can further be characterized as follows:
- RRC_IDLE: The UE has no signaling connection to RAN. This state is used in both LTE and NR SA.
- A UE specific DRX may be configured by upper layers.
- UE controlled mobility based on network configuration.
- The UE Monitors Short Messages transmitted with P-RNTI over DCI.
- The UE Monitors a Paging channel for CN paging using 5G-S-TMSI.
- The UE Performs neighboring cell measurements and cell (re-)selection.
- Acquires system information and can send SI requests (if configured).
- RRC_INACTIVE: The UE has a suspended connection to RAN. This state is used only for NR SA as it requires a 5GC.
- A UE-specific DRX may be configured by upper layers or by the RRC layer.
- UE controlled mobility based on network configuration.
- The UE stores the UE Inactive AS context.
- A RAN-based notification area is configured by the RRC layer.
- The UE Monitors Short Messages transmitted with P-RNTI over DCI.
- The UE Monitors a Paging channel for CN paging using 5G-S-TMSI and RAN paging using full- RNTI.
- The UE Performs neighboring cell measurements and cell (re-)selection.
- The UE Performs RAN-based notification area updates periodically and when moving outside the configured RAN-based notification area.
- The UE Acquires system information and can send SI requests.
- RRC_CONNECTED: The UE has a signaling connection to the RAN. This state is used in both LTE and NR SA.
- The UE stores the AS context.
- Transfer of unicast data to/from UE.
- At lower layers, the UE may be configured with a UE specific DRX.
- For UEs supporting CA, use of one or more SCells, aggregated with the SpCell, for increased bandwidth.
- For UEs supporting DC, use of one SCG, aggregated with the MCG, for increased bandwidth.
- Network controlled mobility within NR and to/from E-UTRA.
- The UE Monitors Short Messages transmitted with P-RNTI over DCI.
- The UE Monitors control channels associated with the shared data channel to determine if data is scheduled for it.
- The UE Provides channel quality and feedback information.
- The UE Performs neighboring cell measurements and measurement reporting.
- The UE Acquires system information.
The reasoning for a new RRC state model in 5G
The RRC States is a solution to the system access, power-saving, and mobility optimization.
- Mission-critical U-MTC UE
– Transmits small packets that require ultra-low latency and/or high reliability. - Massive M-MTC UE
– Wakes up seldom power saving mode to transmit and receive a small payload.
– Camping in a low activity state, and sporadically transmits UL data and/or status reports with a small payload to the network.
– Have periodic and/or sporadic DL small packet transmission.
– Are in the connected state, and sporadically transmit UL data and/or status reports with a small payload to the network. - Smartphones and consumer devices X-MBB UE
– Have periodic and/or sporadic UL and/or DL small packet transmission and extreme data rates.
Some of the characteristics of RRC Connected Inactive are
- The RAN/CN connection is kept, which reduces state transition latency and signaling overhead over the RAN/CN interface.
- UE AS context, e.g. AS security context and DRB/SRB configurations, is stored in the UE and in the RAN. This is crucial to reduce state transition latency and signaling overhead over the air interface.
- UE mobility is based on autonomous cell reselection, where UE may move within its tracking area without updating its location. This leads to lower UE power and network resource consumption, compared to network controlled mobility. Paging is used to reach the UE.
- UE behavior in RRC Connected Inactive state is configured based on the requirements of the applications running in the UE. This can be achieved by providing a service tailored configuration to the UE, e.g. using a dedicated RRC message that transitions the UE to RRC Connected Inactive.
Conclusion
- A new operational state model needed to support connectivity of critical applications, extreme power-saving, and mobility optimization in 5G.
- The efficient way to introduce a new state model is to design a low activity state supporting mobility.
- It is beneficial for the system access if the UEs are always connected to the network and UE context is stored in RAN also during the low activity state.
- A new low activity state should be programmable to support various use cases and requirements, also unforeseeable.