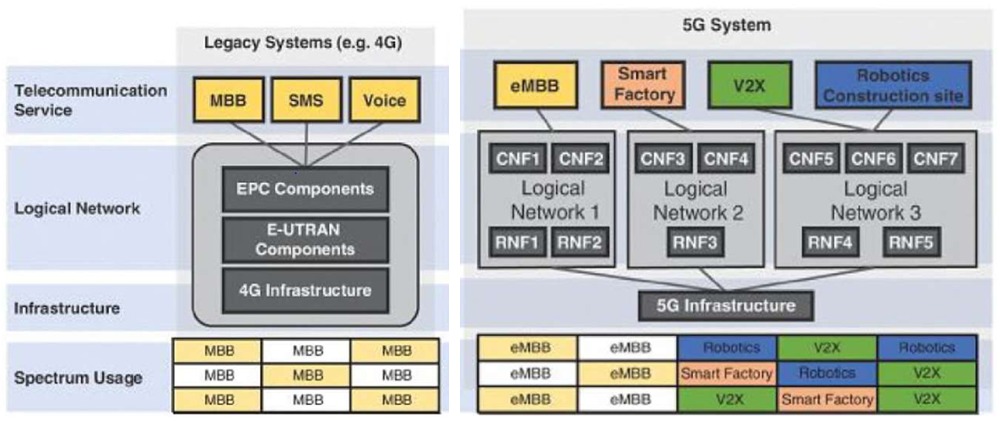
The telecommunications industry sees the new generation of mobile networks, 5G, as a determining growth factor of innovation and automation that will lead to improved competitiveness of businesses and the economy in general. Essentially, it is the basis of success and development in many areas, such as tourism, culture, transportation, agriculture, health, etc.
The crisis example
5G networks are expected to improve telecommunications and user experience in terms of quality, speed, and durability. A first glimpse of this was given during the first wave of the coronavirus pandemic. In this unexpected “stress test” imposed by the lockdown, telecommunication networks were the backbone of digital economic and social activity, fully meeting the increased needs of users, businesses and public administration.
Globally, as an economy and as a society, we are entering a new development age of digitization as a necessity. In order to achieve that, all telecommunications providers, vendors, and the industry need to cooperate and provide converged services on the connectivity of the things brought by the various systems and platforms.
Undoubtedly the resulting lesson is the need for every country to adopt a national reconstruction plan. A crucial aspect of this perspective is the digitalization in the public and private sectors. This requires a common global approach to infrastructure strategy so that the industry may accelerate growth and achieve results in the international digital arena.
Achieving this goal requires continuous and significant investments in network upgrades and service development. Only in the last several years, the telecommunications sector made investments for infrastructure and licensing that cumulatively exceeded billions and continues to invest steadily in the deployment of new networks. Another critical aspect is the preparation of critical sectors of the economy to welcome these investments. This requires a collaborative model and the logic of a comprehensive digital strategy, where everything can happen effortlessly from a single device such as the mobile phone.
Therefore, the notion of a mobile-first digital strategy needs to be adopted by all sectors of the economy. At the same time, the implementation of this digitalization strategy will be supported by adequacy and efficiency from telecommunications networks.
The good thing about this crisis is that we are now talking much more about science and technology. Both functioned as the connecting link that kept us together as a society. On the one hand, we regained the trust in experienced executives and scientists in the field with specialized knowledge. On the other hand, the telecommunication networks kept us in touch with our work, with our wider family and friends, and kept our psychology positive. Professionals, teachers, students, pupils, and citizens, in general, have developed a new mindset and relationship with the networks through teleworking, e-learning services, e-commerce with the State and businesses, e-banking services, etc. Most countries lived for at least two months in a new alternative way, and citizens can now draw a safe conclusion about the telecommunication networks’ potential.
The need for Digital Trasformation
The fact that many countries have succeeded in managing the health crisis allows capitalizing and repositioning their digitalization strategies as a whole. That is, decide which industries to focus on, prioritize, and make the appropriate investments.
In addition, the countries should focus on the commitment of the industry to achieve the goals of sustainable development, as provided by the UN and the EU for 2030 and 2050, where the digitization of the economy is a crucial component. The Telecom industry is part of the “green” solution. ICT infrastructure and services are essential for the whole economy in the green transition. Compared to the climatic footprint of other industries, the footprint of the ICT sector is very low (~ 1.4% of global greenhouse gas emissions). Especially for mobile telephony, the footprint is only ~ 0.4% of greenhouse gas emissions.
According to reports on the Digital Economy and Society Index, large companies are increasingly digitized and are now considered pioneers compared to small and medium-sized enterprises. The vast majority of small and medium-sized enterprises do not yet fully make use of these digital technologies. It is absolutely necessary to give incentives for digital transformation and not just to temporarily meet the needs created by the health crisis.
Through the implementation of an organized and measurable digital strategy, society will be able to take a step further towards digital convergence. Furthermore, countries will be able to modernize their production model and the digital operation of enterprises that make up the core of each country’s business sector.
An effective digitalization that puts emphasis on the user experience and invests in the more productive relationship of citizens and businesses with the public will have as a consequence, the reduction of the operating costs of the State. The most characteristic examples are the higher penetration of digital payments and digitalization in transactions, which reduce losses in public revenue, prevent fraud, and cultivate a sense of security among citizens.
Digitization is also related to the country’s security in general. It is also accompanied by secure personal data but also the successful operation of civil protection during a health crisis. The basis of all these can be a common contact center that operates on advanced technology platforms that allow a range of digital processes and crisis management tools.
There are great opportunities for developing services related to smart cities, smart lighting, better water management, environmental protection, surveillance of marine and terrestrial ecosystems and surveillance for fires, health, education, culture, tourism, with modern means.
The 5G potential
As the 5th generation of mobile telecommunications is evolving, the networks themselves are changing and digitizing as a whole. This results in substantial and qualitative differences compared to the existing ones, leading the rest of the economy and society to digitalization. These software-defined networks, with a new design principle of virtualization, are based on a centralized architecture and will allow flexibility, dynamic allocation, and management, as well as the provision of guaranteed quality of service.
Today we are at the beginning of an industrial revolution that is taking place regarding networks and services. In recent years, data traffic has increased exponentially with specific city hot spots, demanding up to 1 Gbps of wireless bandwidth on mobile devices. In the next several years, these available speeds will reach 10 Gbps.
Furthermore, with the interconnection of tens of millions of devices, there will be 30x more devices connected to the networks that will contribute to the digitization of the whole economy. That is electricity, smart water management, smart meters in cities, traffic management systems, and more. This, in turn, will revolutionize the industry and increase productivity.
5G systems will also uninterruptedly support the operation of service platforms such as smart city services, event management, transport & vehicle support, supply chain services as well as crisis management services or critical infrastructure support.
The transition to the 5G era will change the landscape in telecommunications and society. Extra new features, with high security and personal data protection, can lead modern societies to improved digital performance and a new development model for the whole economy.