Introduction
The Internet of Things (IoT) has transformed how devices interact, enabling unprecedented connectivity and data exchange. In this rapidly evolving landscape, the 3GPP plays a pivotal role by setting standards that ensure interoperability and security across mobile networks. With the release of 3GPP Release 18, significant advancements have been made, particularly in the application layer support for personal IoT networks.
The primary objective of incorporating application layer support for PINs in 3GPP Release 18 is to create a standardized, robust, and scalable framework that can manage the unique requirements of personal IoT devices. This involves several specific goals:
- Improved Interoperability and Integration:
Ensures that personal IoT devices from different manufacturers can seamlessly communicate within a unified network. This facilitates smooth interaction between new IoT devices and existing infrastructure, protecting previous investments.
- Enhanced Device Management:
Enhanced device management is achieved through comprehensive mechanisms for the registration, configuration, and maintenance of IoT devices. Real-time updates and configuration changes allow devices to adapt to evolving user needs and environmental conditions.
- Data Security and Privacy:
Implementing robust security measures such as encryption and authentication to protect data integrity and user privacy. Clear protocols for access management ensure that only authorized entities can interact with personal IoT devices.
- Support for New Use Cases:
Enables innovative applications and services that leverage the unique capabilities of personal IoT devices. This focus on user-centric solutions enhances the user experience by providing intuitive and responsive IoT solutions.
This article delves into the technical enhancements introduced in Release 18, exploring their implications for personal IoT networks and providing insights into real-world applications and future directions.
Evolution and Objectives of Application Layer Support for Personal IoT Networks
The development of Personal IoT Networks (PINs) represents a significant milestone in the evolution of IoT technologies.
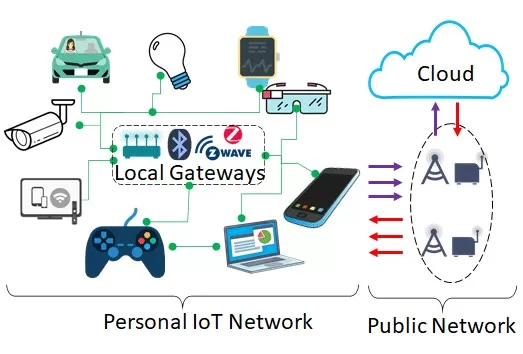
Figure 1: Personal IoT Network and Public Network
The need for interoperability and standardized communication protocols became apparent as the number of connected devices surged. This led to the formation of various consortia and the establishment of standards aimed at ensuring seamless integration and communication among disparate IoT devices.
In 2012, the establishment of oneM2M, a global initiative involving eight leading standards development organizations, marked a critical step in the quest for IoT standardization. This initiative aimed to create a common framework for IoT and M2M (Machine-to-Machine) communications. As the landscape of IoT expanded, the need for more specialized and efficient management of personal IoT devices became clear.
3GPP Release 18 represents a significant advancement in this domain, focusing specifically on enhancing the application layer support for Personal IoT Networks. This evolution has been driven by the increasing complexity and number of consumer IoT devices, ranging from wearable gadgets to smart home appliances.
Technical Architecture of Personal IoT Networks in Release 18
The PIN architecture in 3GPP Release 18 is designed to provide robust, scalable, and secure management and communication for a wide range of personal IoT devices. This architecture incorporates several key components and functionalities, each playing a crucial role in ensuring efficient operation and seamless integration within the broader IoT ecosystem.
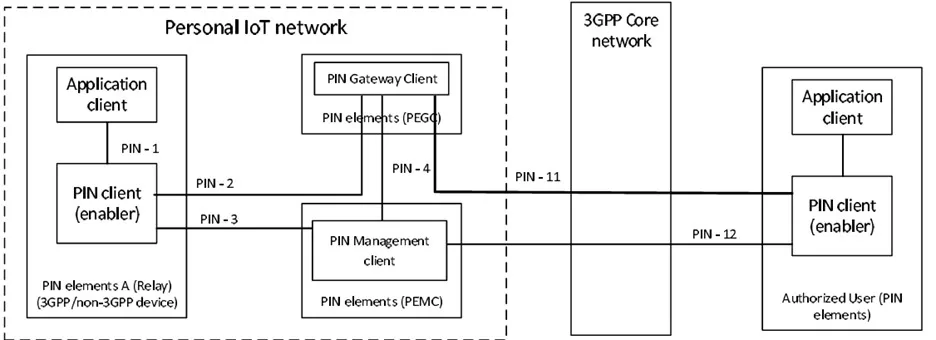
Figure 2: PIN Architecture & Reference point representation
Core Components of PIN Architecture
PIN Client (Enabler)
Deployed within PIN elements, this client facilitates communication and service provision within the PIN. It interacts with application clients and other network components to manage IoT devices effectively.
Application Clients
These are end-user applications or devices such as wearable health monitors, smart home devices, and personal gadgets that interact directly with the IoT network.
Gateway Capability (PEGC)
Serves as the local hub for connecting various personal IoT devices. It ensures local data processing to reduce latency and improve response times for critical applications.
Management Capability (PEMC)
Supports management functions within the PIN, including lifecycle management, configuration, and maintenance of IoT devices. The PEMC provides dynamic configuration capabilities to adapt to evolving user needs and environmental conditions.
Backend Servers
Responsible for long-term data storage, advanced analytics, and centralized control of IoT devices.
Hosts applications that process data from personal IoT networks, providing insights and enabling remote management by users or service providers.
Interaction Model and Reference Points
The architecture is structured around a functional model that defines the interactions between various components through well-defined reference points:
- PIN-1: Interaction between the PIN client and application client, enabling them to provide and consume services within the PIN.
- PIN-2: Communication between PIN clients and PIN gateway clients for data exchange and control.
- PIN-3: Interaction between PIN management clients and PIN clients to manage and configure devices.
- PIN-4: Communication between PIN management clients and PIN gateway clients for management services.
- PIN-11: Interactions between the PEGC and the PIN client of the authorized user.
- PIN-12: Interactions between the PEMC and the PIN client of the authorized user, including configuring policies within a PIN.
- Application Entities (AEs): These entities are responsible for collecting data from sensors, controlling actuators, and providing user interfaces for interaction.
- Common Service Entities (CSEs): Provide essential common service functions like device management, data storage, security, and communication management. They act as intermediaries between AEs and the network layer.
- Network Service Entities (NSEs): Handle connectivity and communication between IoT devices and broader network infrastructure, abstracting underlying network technologies.
This comprehensive architecture ensures that the network can support a wide range of IoT applications with varying requirements, enhancing interoperability, scalability, and security across personal IoT networks.
Key Features of Application Layer Support
The application layer support for Personal IoT Networks (PINs) in 3GPP Release 18 introduces a range of advanced features designed to enhance the functionality, security, and interoperability of personal IoT devices. These features are pivotal in addressing the unique challenges of managing and integrating a diverse array of IoT devices within personal and residential environments. Below are the key features of the application layer support in Release 18:
Lifecycle Management:
- Comprehensive mechanisms for managing the entire lifecycle of IoT devices, including registration, configuration, maintenance, and de-registration.
- Real-time updates and dynamic configuration capabilities allow devices to adapt to changing conditions and user requirements seamlessly.
Dynamic Configuration:
- Devices can receive configuration updates on-the-fly, enabling quick adaptation to new policies or environmental changes.
- Supports remote configuration, reducing the need for manual intervention and ensuring devices operate optimally at all times.
Robust Encryption:
- Implementation of advanced encryption protocols to secure data transmission between IoT devices and backend systems.
- Ensures data integrity and confidentiality, protecting sensitive personal information from unauthorized access.
Authentication and Access Control:
- Strong authentication mechanisms to verify the identity of devices and users accessing the network.
- Mechanisms to anonymize or pseudonymize data where necessary, further safeguarding user privacy.
Standardized Interfaces:
- Utilization of standardized APIs and interfaces to ensure seamless communication between different types of IoT devices and platforms.
- Facilitates the integration of new devices into existing networks without compatibility issues.
Protocol Adaptation:
- Support for multiple communication protocols, enabling devices using different standards to interact within the same network.
- Ensures that legacy devices can coexist with newer technologies, preserving existing investments.
Scalable Architecture:
- Designed to support a large number of devices without compromising network performance.
- Efficient resource management and load balancing to handle increased data traffic and device connectivity.
Innovative Applications:
- Enabling a wide range of new IoT applications by providing the necessary infrastructure and support.
- Examples include advanced health monitoring systems, smart home automation, and enhanced wearable technology.
User-Centric Solutions:
- Focus on enhancing the user experience by providing intuitive and responsive IoT solutions.
- Ensures that personal IoT devices are not only functional but also user-friendly and accessible.
The application layer support for Personal IoT Networks in 3GPP Release 18 introduces a comprehensive set of features designed to enhance device management, security, interoperability, and user experience. These advancements ensure that personal IoT devices can operate efficiently, securely, and seamlessly within an interconnected ecosystem, driving innovation and improving the overall functionality of IoT applications. By addressing the unique challenges of personal IoT networks, these features pave the way for a more connected and intelligent future.
Use Case: Home Automation
The application layer support for Personal IoT Networks (PINs) in 3GPP Release 18 facilitates a wide range of real-world applications, enhancing the functionality, security, and interoperability of IoT devices across various domains. In the case of Integrated Home Automation, we can highlight the following benefits:
- The application layer provides seamless integration of various smart home devices, including lighting systems, thermostats, security cameras, and appliances.
- Enhanced interoperability allows for unified control and automation through a single platform, improving convenience and energy efficiency.
In the diagram below, we are illustrating a setup where multiple devices within the home connect to a central hub. These connections can be direct or through a relay. A smartphone integrated into the 5G system can receive notifications about various events, such as a door opening, from the home automation PIN.
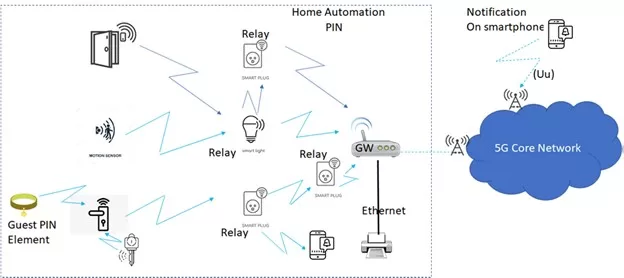
Figure 3: Illustration of Home Automation with PIN
The application layer support for PIN makes IoT devices work better, safer, and easier together, as shown in the home automation diagram. This update improves smart homes by letting devices like smart plugs and motion sensors connect to a central hub directly or through relays.
For example, when a door opens, a notification can be sent to a smartphone through the 5G core network. These improvements not only make personal IoT networks more efficient and responsive but also create a more connected and user-friendly IoT environment for various uses, from homes to industries.
Conclusion
The introduction of application layer support for Personal IoT Networks (PIN) in 3GPP Release 18 represents a significant advancement in the management and integration of IoT devices. This standardized framework addresses the growing complexity and diversity of personal IoT devices, providing robust solutions for improved interoperability, enhanced device management, and stringent data security. The technical architecture, with its layered approach and defined reference points, ensures efficient operation and seamless integration within the broader IoT ecosystem.
The key features introduced in Release 18, such as lifecycle management, dynamic configuration, and robust encryption, are pivotal in enhancing the functionality and security of personal IoT networks. These advancements not only facilitate the integration of various devices and platforms but also pave the way for innovative applications and user-centric solutions, driving the evolution of smart homes, healthcare, and other domains.
In conclusion, the advancements in application layer support for PINs in 3GPP Release 18 are poised to drive significant innovation and efficiency across various IoT applications. By addressing the unique challenges of personal IoT networks, these enhancements contribute to a more connected, intelligent, and user-friendly IoT ecosystem, ultimately improving the quality of life and operational efficiency in diverse settings.
References
- 3GPP TS 23.542 “Application layer support for Personal IoT Network”, version 18.3.0, Release 18, 2024
- 3GPP TS 23.700-88, “Study on architecture enhancements for Personal IoT Network (PIN)”, Release 18, 2023