Introduction
Personal IoT Networks (PIN) represent a transformative concept within the realm of 5G technology, tailored to address the Internet of Things (IoT). PINs are specifically designed networks that cater to individual users’ IoT devices, providing a customized and efficient ecosystem for managing a multitude of personal IoT applications. These networks are crucial in the IoT ecosystem, as they offer a personalized approach to IoT connectivity, allowing users to seamlessly integrate and manage their devices. The emergence of PINs signifies a shift towards more user-centric IoT solutions, where ease of use, customization, and efficient device management are paramount.
Overview of PIN Architecture
The architecture of PIN in 5G frameworks presents varied deployment models, each aligning with specific operational needs and spectrum accessibility.
The Mobile Operator Network, leveraging both public licensed network facilities and Multi-access Edge Computing (MEC), can extend its reach through shared or licensed spectrum, mitigating the need for extensive infrastructure investment.
On the other hand, Managed Service Providers can operate PINs in private networks on shared or dynamic spectrum access, offering tailored services from private clouds. These diverse configurations—from dedicated licensed spectrum setups for localized LAN Systems and Small Cells to unlicensed spectrum models—illustrate the flexibility of PINs in accommodating a broad range.
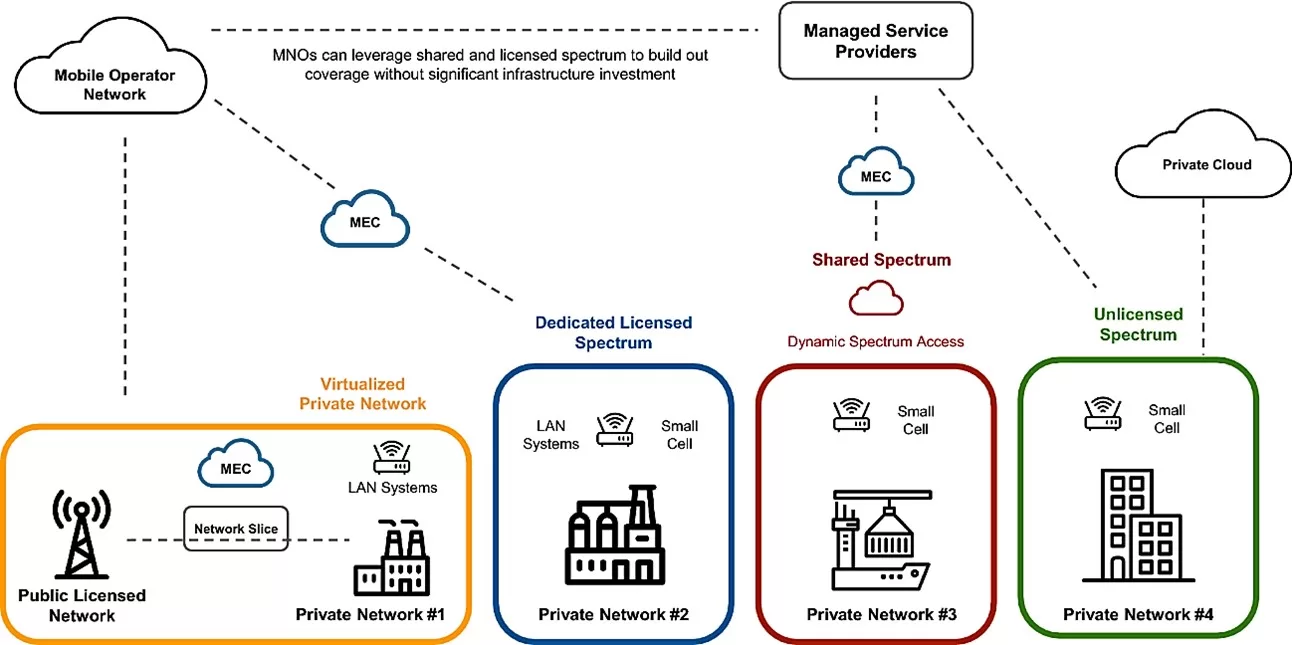
Figure 1: PIN Architecture
In this architecture, multiple deployment scenarios are possible, reflecting the adaptability of 5G to various operational needs.
Architectural Enhancements for PIN in Release 18
Release 18 brings comprehensive architectural enhancements to Personal IoT Networks (PIN), focusing on specific aspects:
- Enhanced Management of PIN Elements: A significant update is the refined management of PIN Elements, including devices with or without gateway capabilities. This refinement allows for better control and efficiency in device management within the network.
- Advanced Communication Pathways: Improved communication pathways within a PIN are introduced, facilitating more efficient direct communication between PIN Elements and interactions with the broader 5G network.
- Robust Security Framework: The security framework for PINs is strengthened to ensure the safety and privacy of data within these networks. This includes enhanced mechanisms for authentication and authorization of PIN and its elements.
- Policy and Parameter Provisioning: Provisions for setting and managing policies and parameters within a PIN are enhanced, enabling more precise control over network behavior and performance.
- Streamlined Identification Processes: The process for identifying a PIN and its elements in the 5G Core (5GC) is made more efficient, improving the overall management and operability of the PIN in the 5G ecosystem.
These enhancements collectively elevate the functionality of PINs in Release 18, ensuring they are better equipped to meet the demands of modern IoT applications.
Deployment of PIN
The deployment of Personal IoT Networks (PIN) in 5G Release 18 encompasses various models:
- Ownership and Management Models: PIN can be owned and managed by enterprises themselves or by Mobile Network Operators (MNOs). This flexibility allows for tailored network management according to the specific needs of the enterprise.
- Spectrum Utilization: PIN deployment can utilize different spectrum types – licensed, unlicensed (such as NR-U, LAA), or license-shared (like CBRS, LSA). This choice depends on the specific requirements of the deployment scenario.
- Deployment Choices: Options range from standalone private networks to those combined with public MNO networks. Factors influencing this choice include the spectrum owner, QoS requirements, and the physical scope of deployment (single or multiple premises).
- 3GPP Characteristics for Private 5G: Defined features in 3GPP standards facilitate the use of private 5G as a viable alternative to Wi-Fi 6 or wired solutions in the private sector. These include security features, flexible spectrum access methods, and high-performance characteristics suitable for URLLC in industrial IoT (IIoT).
- Types of Private 5G Deployments: These include independent private 5G LANs (by an enterprise or MNO), RAN and signaling shared networks, network slicing, and RAN and control plane sharing setups.
Each deployment option offers unique advantages and is chosen based on specific enterprise needs, regulatory environments, and technological requirements.
The table below provides a technical snapshot of the various deployment options for PIN in Release 18, highlighting the differences in spectrum use, management, quality of service, and network architecture.
Table 1: Deployment models
| Deployment Model | Spectrum Type | Management Entity | QoS Features | Architecture Specifics |
| Independent Private 5G LAN (Enterprise) | Local 5G Frequency | Enterprise | Customizable | Isolated 5G network, UDM, 5G Core CP, UPF, gNB |
| Independent Private 5G LAN (MNO) | Licensed 5G Frequency | MNO | Standard MNO QoS | MNO-built and operated, similar to enterprise model |
| RAN and Signaling Shared | Shared with Public Network | MNO & Enterprise | Mixed | UDM, 5G Core CP and UPF local; gNB and spectrum shared |
| Network Slicing (RAN & Core Sharing) | Shared with Public Network | MNO | E2E Network Slicing | Logically detached 5G Core and RAN; UPF, UDM in MNO’s cloud |
PIN Element Management and Control in Release 18
The advancements in Release 18 bring a comprehensive upgrade to the management and control of PIN Elements, key components in PIN:
- Refined Element Configuration and Management: The new release introduces a more sophisticated approach to configuring and managing PIN Elements. This includes improved protocols for device setup, easier integration of new devices, and more intuitive user interfaces for network administrators. These changes facilitate seamless management of diverse IoT devices within the PIN.
- Enhanced Communication Protocols: Control over communication channels between PIN Elements, and their interaction with external networks, is significantly enhanced. This involves advanced routing algorithms, optimized data transfer mechanisms, and better support for varying communication standards. These enhancements ensure that data transmission within the PIN is both efficient and secure.
- Dynamic Element Integration: The integration process for new PIN Elements has been streamlined, making it faster and more user-friendly. This ease of integration is crucial for rapidly evolving IoT environments where new devices are frequently added to the network.
- Security and Access Management: A key focus in Release 18 is the bolstered security management for PIN Elements. This includes enhanced encryption protocols, rigorous access controls, and comprehensive security monitoring. These features are crucial for protecting sensitive data and preventing unauthorized access to the network.
- Automated Network Optimization: The introduction of automated mechanisms for network optimization ensures that PIN Elements operate at optimal efficiency. This includes self-adjusting network parameters based on real-time data analysis, which contributes to overall network performance and reliability.
- Customization and User Control: Users are provided with more options to customize and control their PIN Elements. This level of customization allows users to tailor network settings to their specific needs and preferences, enhancing the overall user experience.
The upgrades in PIN Element management and control in Release 18 represent a significant leap forward in the evolution of Personal IoT Networks, offering enhanced efficiency, security, and user-friendliness. These improvements are instrumental in enabling more robust and versatile IoT environments.
Security and Privacy in PIN
In Release 18, significant strides have been made in enhancing the security and privacy of Personal IoT Networks (PIN):
- Advanced Encryption Protocols: The new release integrates state-of-the-art encryption techniques, significantly bolstering the security of data transmission within PINs. This ensures that sensitive information, typical in IoT applications, remains protected from external threats.
- Robust Access Control Mechanisms: Enhanced access control mechanisms are implemented to ensure that only authorized devices and users can access the network. This minimizes the risk of unauthorized intrusion, a critical aspect in maintaining the integrity and privacy of the network.
- Network Segmentation and Isolation: The architecture allows for the creation of segmented network zones, isolating certain areas or devices within the PIN. This segmentation is crucial for containing potential security breaches and limiting their impact on the entire network.
- Continuous Monitoring and Threat Detection: The introduction of sophisticated monitoring tools in PINs enables the continuous scanning of the network for any suspicious activities, ensuring prompt detection and mitigation of potential threats.
These security and privacy enhancements in PIN under Release 18 are designed to address the evolving challenges in IoT security, ensuring that Personal IoT Networks remain secure and resilient against a backdrop of increasing cyber threats.
Use Cases and Applications
With the advancements in Personal IoT Networks (PIN) in Release 18, a plethora of use cases and applications emerge, showcasing the versatility and potential of this technology:
- Smart Home Systems: PINs can efficiently manage a network of smart home devices, ensuring seamless communication and enhanced security for home automation systems.
- Personal Health Monitoring: In healthcare, PINs facilitate remote health monitoring, allowing for real-time data collection and analysis from wearable health devices.
- Automotive Applications: PINs can be integrated into vehicular systems for improved vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication, enhancing features like autonomous driving and in-vehicle infotainment.
- Agricultural IoT: In agriculture, PINs enable precise monitoring and control of farming equipment and environmental sensors, contributing to smart agriculture solutions.
- Retail and Inventory Management: Retail sectors can utilize PINs for efficient inventory tracking and customer engagement through IoT-enabled devices.
These applications demonstrate the broad scope of PINs in enhancing connectivity and functionality across various domains, significantly contributing to the growth and efficiency of IoT solutions.
Conclusion
As 5G technology evolves, Personal IoT Networks (PIN) stand at the forefront of this transformation, particularly with the architectural enhancements introduced in Release 18. These advancements not only refine the control and management of IoT devices but also significantly bolster network security and privacy, ensuring the protection of sensitive data.
The deployment models presented, ranging from enterprise-owned to MNO-managed networks, offer flexibility and cater to various operational needs and spectrum access requirements. With these developments, Release 18 of PIN is poised to support a wide array of IoT applications, from smart home systems to precision agriculture, demonstrating the vast potential of 5G to enhance connectivity and functionality across different domains. As the technology matures, the continued focus on overcoming deployment challenges will further solidify the role of PIN in the burgeoning IoT landscape.
References
- 3GPP Specification #23.700-88, “Study on architecture enhancements for Personal IoT Network (PIN)”, Release 18, 2023
- Eswaran, S., Honnavalli, P. Private 5G networks: a survey on enabling technologies, deployment models, use cases and research directions. Telecommun Syst82, 3–26 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-022-00978-z