Abstract
The convergence of Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) and the 5G wireless technology is poised to reshape industries, catalyzing the era of Industry 4.0. As manufacturing processes, supply chains, and industrial operations become increasingly digitized, the need for robust, low-latency, and reliable communication networks has never been more critical.
In this article, we embark on a journey to explore how 5G, with its enhanced capabilities introduced in 3GPP Release-16 and Release-17, is set to revolutionize Industrial IoT. The seamless integration of the 5G system with IEEE 802.1 specifications, the advent of Time Sensitive Networking (TSN), and the inception of Non-Public Networks (NPN) usher in a new era of industrial connectivity.
What is Industrial IoT?
Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) refers to the integration of internet-connected sensors, devices, machines, and systems within industrial environments to enhance operational efficiency, productivity, and decision-making. Unlike traditional Internet of Things (IoT), which primarily focuses on consumer-oriented applications like smart homes and wearable devices, IIoT is tailored for industrial sectors such as manufacturing, energy, agriculture, healthcare, and transportation.
IIoT leverages advanced technologies such as sensors, data analytics, artificial intelligence (AI), and cloud computing to gather, analyze, and share data from various industrial processes and assets. This data-driven approach enables organizations to monitor equipment performance, predict maintenance needs, optimize workflows, and make informed decisions to improve overall operational outcomes.
In 2021, the worldwide market size for industrial IoT was appraised at approximately USD 326.1 billion. It is projected to reach about USD 1742.8 billion by 2030, showcasing a notable Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 20.47% over the forecast span from 2022 to 2030.
The rapid growth of the global industrial IoT market is driven by its ability to provide timely insights for smarter decision-making across industries. Technological advancements in semiconductors, coupled with cost-effective sensors and processors, enable real-time data access, while the integration of AI and IoT in manufacturing optimizes processes and enhances quality control. This convergence is boosting the market’s expansion.
Integrating Industry and Connectivity (Rel-16)
The advent of Industry 4.0 brings forth a paradigm shift in industrial processes, emphasizing automation, data exchange, and digital transformation. Central to this transformation is the integration of industrial systems with cutting-edge communication technologies, and here, 5G takes the center stage. The 3GPP Release-16 introduces a groundbreaking initiative known as ‘Vertical_LAN,’ designed to seamlessly merge the 5G system with the IEEE 802.1 specifications, particularly focusing on Time Sensitive Networking (TSN).
5G Time Sensitive Communications
Time-sensitive communication is at the heart of Industry 4.0, where machines, devices, and systems must interact in a synchronized manner with minimal latency.
The integration of the IEEE TSN framework with the 5G system paves the way for deterministic and low-latency communication in the factories of the future. The concept of 5G Time Sensitive Communication emerges, offering support for deterministic and/or isochronous communication with impeccable reliability and availability.
This service provides packet transport with Quality of Service (QoS) attributes, including bounded latency and reliability.
Key to achieving deterministic communication is synchronization. The entire 5G system operates as an IEEE 802.1AS “time-aware system,” ensuring synchronization across elements like UE, gNB, UPF, NW-TT, and DS-TTs. The synchronization process revolves around the 5G GM, maintaining tight coordination to eliminate communication delays.
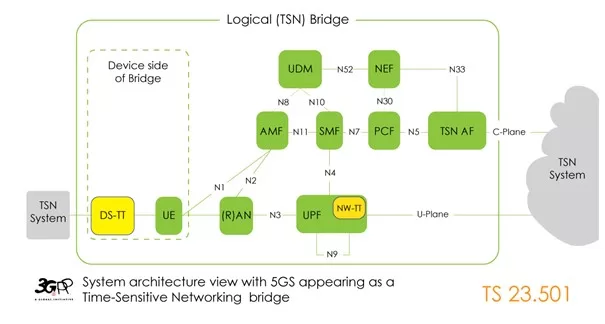
At the edges of the 5G system, TSN Translators (TTs) assume a pivotal role. These TTs facilitate IEEE 802.1AS operations, ensuring time synchronization and deterministic traffic pattern delivery. The collaboration between 5G and TSN components ensures that the data flows seamlessly, meeting the stringent timing demands of industrial applications.
The integration of (g)PTP synchronization allows for uplink and downlink synchronization scenarios. Whether the Grand Master clock is located behind the UE or the network, the 5G System caters to both configurations. This flexibility ensures that regardless of the deployment model, time-sensitive communication remains accurate and reliable.
5G Non-Public Network (NPN)
The idea of a Non-Public Network (NPN) within the 5G realm is revolutionary. It encompasses both Stand-alone Non-Public Networks (SNPN) and Public Network Integrated NPN (PNI-NPN).
- Stand-alone Non-Public Networks (SNPN)
SNPNs operate independently of traditional Public Land Mobile Networks (PLMN). They are identified by a combination of PLMN ID and NID (Network Identifier). SNPN-enabled User Equipment (UE) is configured with subscriber credentials for each subscribed SNPN. This configuration enables efficient and secure communication tailored to the industry’s requirements.
- Public Network Integrated NPN (PNI-NPN)
PNI-NPNs, on the other hand, are non-public networks that leverage the support of a PLMN. They are identified by PLMN ID and Closed Access Group (CAG) ID. CAG cells within PNI-NPNs broadcast identifiers that ensure only UEs compatible with the network’s specifications gain access. This integration retains the benefits of PLMN infrastructure while catering to industrial demands.
The architecture accommodates various NPN deployment models and introduces the notion of Self-assignment and Coordinated assignment for Network Identifiers (NID), ensuring uniqueness and efficient network access control.
As the industrial landscape evolves, so do the connectivity requirements. 3GPP Release-16 recognizes the need for tailored communication networks, giving rise to 5G Non-Public Networks (NPN).
3GPP Release-16 introduces flexible assignment models for NIDs, enabling industries to choose between self-assignment or coordinated assignment. This empowers industries to configure their network based on their unique needs while maintaining a cohesive numbering structure.
Revolutionizing 5G LAN Services
Industries are on the brink of a connectivity revolution, and 5G LAN-type services, introduced in 3GPP Release-16, stand at the forefront of this transformation. These services bridge the gap between traditional Local Area Networks (LANs) and the advanced capabilities of 5G, ushering in a new era of efficiency and innovation.
5G LAN-type services extend the functionalities of LANs and Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) with the cutting-edge capabilities of 5G technology. By harnessing the power of 5G, these services offer a range of features including high performance, long-distance access, mobility, and enhanced security.
At its core, the 5G LAN-type service enables the management of Virtual Network (VN) Group identification, membership, and associated data. This management can be carried out by network administrators or even dynamically by third-party applications (AF).
One of the hallmark features of 5G LAN-type services is the dynamic management of VN Groups. The Network Exposure Function (NEF) plays a pivotal role in exposing a suite of services for managing VN Groups. This dynamic management ensures that the network adapts to changing requirements, allowing for seamless scaling and customization.
The NEF exposes services that enable the addition, deletion, and modification of 5G VN Groups and their members. This exposure ensures that network operators and administrators have the tools to fine-tune the network configuration to suit their needs.
Release-17’s Industrial IoT Enhancements
Building upon the solid foundation established in Release-16, the 3GPP community has once again propelled the evolution of Industrial Internet of Things (IoT) connectivity with a series of enhancements in Release-17. These enhancements are designed to amplify the capabilities of the 5G System, further cementing its role as a transformative force in the realm of industrial communication.
- Extending Time Synchronization and Time Sensitive Communications
One of the focal points of Release-17 is the extension of time synchronization and time-sensitive communication capabilities. Recognizing the critical role of these functionalities in industrial settings, 3GPP has worked diligently to expand their scope and effectiveness.
- 5GS Synchronization and (g)PTP Domain Synchronization
Rel-17 introduces a dual approach to time synchronization, encompassing both 5GS synchronization and (g)PTP domain synchronization. This approach accommodates the diverse requirements of different industrial scenarios, ensuring that time-sensitive operations are executed with impeccable precision.
In alignment with IEEE standards, the 5G System operates in various (g)PTP time synchronization modes, ranging from time-aware systems to different clock configurations. This versatile approach empowers industries to choose the mode that best aligns with their specific synchronization needs.
- Empowering Application Functions (AFs)
Rel-17 places a greater emphasis on enabling Application Functions (AFs) to actively contribute to the orchestration of time synchronization and time-sensitive communications. This engagement ensures that AFs can provide critical input, requirements, and parameters, aligning the 5G System more closely with the needs of industrial applications.
The enhancements introduced in Release-17 represent a pivotal step forward in the evolution of Industrial IoT connectivity within the 5G System. By combining the power of time synchronization, optimized communication, and network customization, these enhancements equip industries with the tools they need to usher in a new era of industrial innovation.
Efficient Traffic Flow: TSC QoS
A cornerstone of the 5G System’s transformative potential for Industrial IoT is its capacity to manage traffic with unparalleled efficiency. This efficiency is particularly evident in the realm of Time Sensitive Communication (TSC), where the Quality of Service (QoS) optimization takes center stage. The integration of Time Sensitive Communication Assistance Information (TSCAI) in Release-17 is a testament to 3GPP’s commitment to unlocking the full potential of industrial connectivity.
Unveiling TSCAI: Elevating QoS Optimization
TSCAI encapsulates crucial traffic pattern parameters, including burst arrival time, periodicity, flow direction, and survival time. This information empowers the 5G Access Network (5G-AN) to optimize the scheduling of deterministic traffic flows, minimizing latency and ensuring impeccable communication performance.
The power of TSCAI materializes through multiple scheduling mechanisms, including Configured Grants, Semi-Persistent Scheduling, and Dynamic Grants. These mechanisms enable the 5G System to accommodate varying traffic characteristics and priorities, ensuring that different industrial communication requirements are met with precision.
By harmonizing burst patterns, maintaining timing consistency, and intelligently allocating resources, TSCAI transforms communication into a seamless, efficient, and highly reliable process. The result is an Industrial IoT landscape that thrives on precision, predictability, and unprecedented connectivity, fostering an era of innovation and efficiency.
Future of Industrial IoT
The journey of Industrial IoT within the 5G System has traversed significant milestones, each amplifying the capabilities of industries worldwide. As we gaze into the future, a landscape of boundless possibilities emerges, driven by the fusion of 5G connectivity and industrial innovation. The future of Industrial IoT is poised to reshape industries, factories, warehouses, and remote facilities will seamlessly communicate, fostering real-time collaboration, predictive maintenance, and efficient resource management.
- Precision Automation: Machines as Partners
The synergy between 5G and Industrial IoT paves the way for precision automation. Machines will transcend their role as tools and become collaborative partners in the production process. Armed with real-time data and instantaneous communication, machines will adapt, optimize, and elevate the efficiency of industrial workflows.
- Autonomous Intelligence: From Insight to Action
The convergence of AI and 5G within the Industrial IoT ecosystem will give rise to autonomous intelligence. AI-driven analytics will swiftly process massive datasets, deriving actionable insights in real time. These insights will enable proactive decision-making, predictive maintenance, and the swift resolution of anomalies.
- Customization at Scale: Redefining Products
Mass production will be replaced by mass customization, where products are tailored to individual requirements. 5G-enabled real-time data exchanges will allow manufacturers to adjust product specifications on the fly, catering to the diverse demands of the market.
- Sustainability Enhanced
The symbiosis of 5G and Industrial IoT will propel sustainable practices to new heights. Energy consumption, resource allocation, and waste management will be intricately monitored and optimized, minimizing the environmental footprint of industries worldwide.
- Security and Regulation
Security concerns surrounding data privacy, intellectual property, and network vulnerabilities will necessitate robust encryption, authentication, and cybersecurity frameworks. Harmonizing global regulations to facilitate seamless cross-border operations will also be a critical task.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the convergence of IIoT and 5G is reshaping industries into Industry 4.0. This is driven by the need for robust communication networks for digitized processes. The integration of 5G with IEEE 802.1, TSN, and NPN is powering this revolution.
Release-17 extends time synchronization and communication capabilities, empowering Application Functions (AFs). This equips industries with tools for a new era of innovation.
Efficient traffic flow in 5G is crucial for IoT. TSCAI optimizes the Quality of Service, enhancing communication efficiency.
In the future, 5G and Industrial IoT promise precision automation, autonomous intelligence, customization, sustainability, and security. Industries are poised for real-time collaboration, predictive maintenance, and efficiency, redefining business operations. Addressing data privacy, intellectual property, and regulations will be crucial for success.
References
- 3GPP TS 23.501, System Architecture for 5G System
- 3GPP TS 23.502, Procedures for 5G System
- https://www.precedenceresearch.com/industrial-iot-market

