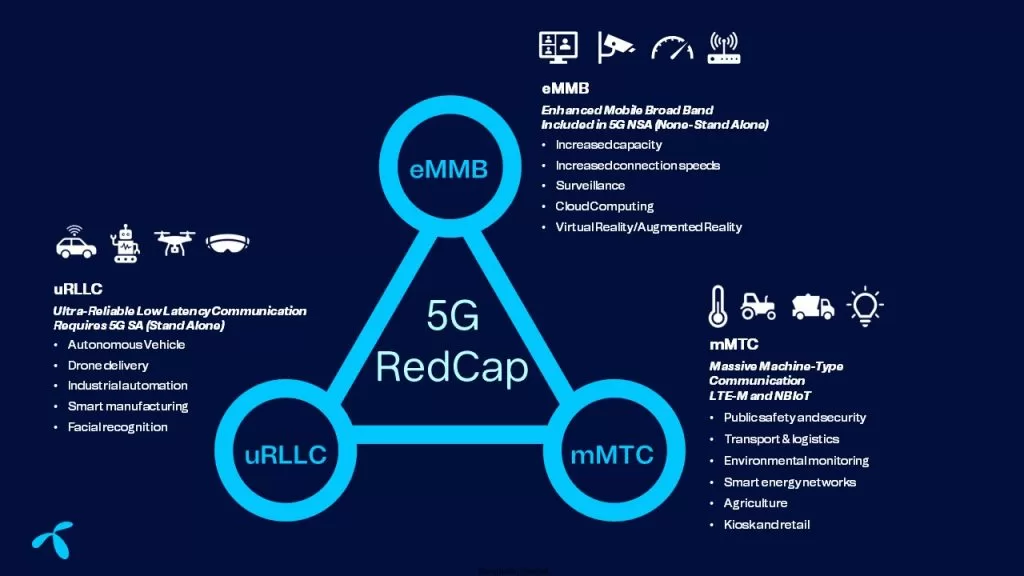
Introduction
The advent of 5G New Radio (NR) has ushered in a new era of connectivity, promising to revolutionize a wide array of applications from high-speed mobile internet to the Internet of Things (IoT). While 5G NR is designed to deliver ultra-reliable, low-latency communication (URLLC) and enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB), there exists a spectrum of IoT applications that demand a tailored approach. These applications, often described as mid-tier, require connectivity solutions that strike a balance between performance and efficiency—beyond what traditional LTE-M and NB-IoT can offer, yet not as resource-intensive as full-fledged 5G solutions.
Enter 5G NR Light, also known as Reduced Capability (RedCap) technology. Introduced in 3GPP Release 17, NR-RedCap is engineered to address this very gap, offering a solution that caters to devices and applications requiring moderate data rates, extended battery life, and reduced complexity and cost. This technology is pivotal for enabling a wide range of IoT applications, from industrial automation and smart grids to wearables and sensor networks, which do not necessitate the high throughput or ultra-low latency of eMBB or URLLC but still benefit from the advancements of 5G NR technology.
NR-RedCap represents a significant step forward in making 5G accessible to a broader array of devices and applications by simplifying device requirements and optimizing power consumption, all while ensuring compatibility with the existing 5G infrastructure. As such, it fills a critical niche in the 5G ecosystem, providing a connectivity solution that is both powerful and efficient, tailored to the unique needs of mid-tier IoT applications.
With Release 18, dubbed “5G Advanced,” the technology receives a series of upgrades and new features aimed at expanding its capabilities and improving its integration within the 5G network. These enhancements are designed to refine the performance, efficiency, and flexibility of NR-RedCap, ensuring that it remains a key enabler of IoT connectivity in the 5G era.
NR-RedCap in the 5G Landscape
The introduction of NR-RedCap technology, particularly from 3GPP Release 16 onwards, has significantly reshaped the 5G landscape, creating a new tier of connectivity that caters specifically to the nuanced requirements of mid-tier IoT applications. Positioned strategically within the spectrum of 5G services, NR-RedCap serves as a bridge between the capabilities of LTE-M/NB-IoT and those of eMBB/URLLC, offering a balanced solution that addresses the unique challenges faced by a wide array of IoT deployments.
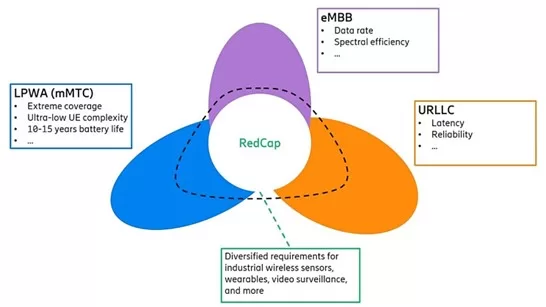
NR-RedCap is designed to fill a critical gap in the 5G ecosystem, providing a connectivity option that is more robust than LTE-M and NB-IoT but less complex and power-intensive than eMBB and URLLC.
The key to NR-RedCap’s positioning lies in its ability to offer:
- Enhanced Data Rates: While not aiming for the peak data rates of eMBB, NR-RedCap supports higher throughput than LTE-M and NB-IoT, making it suitable for applications like video surveillance and industrial sensors that transmit richer data.
- Extended Battery Life: By optimizing power consumption, NR-RedCap extends the battery life of IoT devices, a critical feature for deployments in remote or inaccessible locations.
- Simplified Device Architecture: NR-RedCap reduces the complexity and cost of devices by scaling down certain 5G NR features, making 5G connectivity accessible for a broader range of IoT applications.
To understand the unique value proposition of NR-RedCap, it’s essential to compare it with the other tiers of connectivity within the 5G and LTE landscapes:
- LTE-M and NB-IoT: These technologies are tailored for low-power wide-area network (LPWAN) applications, focusing on minimal data rates and maximal battery life. While they serve the needs of basic IoT sensors and trackers well, they fall short for applications requiring higher throughput or lower latency.
- eMBB: Aimed at delivering high data rates and supporting bandwidth-intensive applications, eMBB exceeds the requirements and capabilities necessary for many IoT applications, leading to unnecessarily high costs and complexity.
NR-RedCap, therefore, emerges as an optimal solution for applications that lie in the middle of this spectrum, requiring more than what LTE-M/NB-IoT can offer but less than the full capabilities of eMBB/URLLC. This includes a wide range of industrial, commercial, and consumer applications that benefit from moderate data rates, improved latency, and enhanced connectivity without the need for the high throughput and ultra-reliability offered by eMBB and URLLC, respectively.
Evolution of NR-RedCap: From Release 16 to Release 18
The evolution of NR-RedCap technology through the 3GPP releases marks a significant trajectory of innovation aimed at refining and expanding the capabilities of 5G to cater to a broader spectrum of IoT applications.
Table 1: Overview of Technology Features
| Technology Feature | New Radio Enhanced Mobile Broadband (Release 15/16) | New Radio Reduced Capability (Release 17) | New Radio Reduced Capability (Release 18) |
| Bandwidth for Device | 100 Megahertz (FR1) 200 Megahertz (FR2) | 20 Megahertz (FR1) 100 Megahertz (FR2) | 20 or 5 Megahertz (FR1 only) |
| Signal Duplication | Full Duplex/Half Duplex, Time Division | Full Duplex/Half Duplex, Time Division | Full Duplex/Half Duplex, Time Division |
| Antenna Type | Single Transmitter, Dual Receiver / Dual Transmitter, Single Receiver | Single Transmitter, Single Receiver / Dual Transmitter, Single Receiver | Single Transmitter, Single Receiver / Dual Transmitter, Single Receiver |
| Highest Modulation | 256-level QAM for Downlink, 64-level QAM for Uplink | 64-level QAM (256 optional) | 64-level QAM (256 optional) |
| Max Data Speed (DL) | 2.3 Gigabits per second | 220 Megabits per second | 10 Megabits per second |
| Max Data Speed (UL) | 468 Megabits per second | 120 Megabits per second | 10 Megabits per second |
With Release 15/16, the enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB) aspect of 5G New Radio set the stage for robust high-speed communication, boasting downlink speeds of up to 2.3 Gbps and uplink speeds of up to 468 Mbps. This release paved the way for IoT devices requiring high throughput and laid the groundwork for the next iterations of NR technology.
Release 17 established the foundational framework for NR-RedCap by streamlining the expansive features of 5G NR to cater to IoT devices needing moderate throughput, lower complexity, and increased battery life. The focus was on enabling IoT applications that do not demand the full spectrum of 5G capabilities yet benefit from the advancements in 5G technology.
As we look to Release 18, NR-RedCap is poised for a series of enhancements that build upon the Release 17 specifications to address the evolving demands of the IoT landscape. Although still in the development phase, with Release 18 expected to offer peak data rates of 10 Mbps for both downlink and uplink, these enhancements are projected to include:
- Further Reduction in Device Complexity: By further simplifying device architecture, NR-RedCap aims to become even more cost-effective and power-efficient, making the technology more accessible for a diverse array of IoT devices.
- Enhanced Network Integration: With improvements in how NR-RedCap devices integrate with existing 5G networks, there is an emphasis on efficient network resource utilization and simplified operational deployments for service providers.
- Advanced Power Saving Techniques: New power-saving features are anticipated, which will be crucial in extending the battery life of IoT devices, especially those in remote or hard-to-reach areas.
- Increased Deployment Flexibility: The introduction of more varied configuration options for NR-RedCap will support an expanded range of use cases, accommodating specific coverage or capacity needs.
The transition from Release 17 to Release 18 signifies a concerted effort within the industry to refine NR-RedCap technology. These efforts demonstrate the industry’s commitment to meeting the varied requirements of the IoT ecosystem. With each subsequent release, 3GPP continues to refine NR-RedCap, ensuring that 5G remains a versatile and comprehensive platform for connectivity, capable of supporting a wide spectrum of IoT applications, from basic sensors to intricate industrial automation systems.
Challenges and Limitations
While NR-RedCap technology presents a promising solution for mid-tier IoT applications, bridging the gap between high-end 5G capabilities and the needs of devices requiring less complexity and power consumption, its deployment and widespread adoption are not without challenges and limitations. Understanding these hurdles is crucial for stakeholders across the telecommunications and IoT ecosystems as they strategize to leverage NR-RedCap effectively.
Device Certification and Standardization
The process of certifying NR-RedCap devices to ensure they meet the necessary standards and interoperability requirements can be time-consuming and resource-intensive. This certification process is critical to guarantee that NR-RedCap devices can operate seamlessly within the 5G ecosystem, but it requires ongoing effort and collaboration between industry players and regulatory bodies.
Network Infrastructure Adaptation
For mobile operators, integrating NR-RedCap into existing network infrastructures requires careful planning and investment. This adaptation process is essential to maximize the efficiency and effectiveness of NR-RedCap deployments but represents an upfront cost and operational challenge for network operators.
Coverage and Performance Expectations
Ensuring that NR-RedCap devices deliver consistent performance and adequate coverage, especially in challenging environments or at the edge of network coverage areas, remains a challenge. While enhancements in Release 18 aim to improve coverage and device efficiency, meeting the diverse and sometimes conflicting expectations of various IoT applications requires ongoing optimization and innovation. Balancing performance, coverage, and power efficiency to meet the specific needs of different use cases is an ongoing challenge for NR-RedCap technology.
Conclusion
This article elucidates the development and importance of NR-RedCap in enhancing 5G connectivity for mid-tier IoT applications. NR-RedCap addresses the need for a connectivity solution that balances moderate data rates, extended battery life, and reduced complexity at a lower cost. It serves as a crucial bridge within the 5G landscape, positioned between the capabilities of LTE-M/NB-IoT and eMBB/URLLC, tailored for IoT applications that benefit from 5G advancements without requiring full eMBB or URLLC capabilities.
The enhancements in Release 18 aim to simplify device architecture, improve network integration, introduce power-saving features, and offer flexible deployment options, addressing the evolving IoT demands. Despite its potential, NR-RedCap faces challenges such as device certification, network adaptation, and ensuring consistent performance across diverse environments. Overcoming these challenges is essential for leveraging NR-RedCap’s full potential as a key facilitator of IoT connectivity in the 5G era, underscoring the need for continued industry collaboration and innovation.
References
- Xingqin Lin, “An Overview of 5G Advanced Evolution in 3GPP Release 18”, IEEE Communications Standards Magazine
- 3GPP TR 23.700-68, “Study on RedCap Phase 2”, 2023
- Matteo Pagin et al, “5G NR-Light at Millimeter Waves: Design Guidelines for Mid-Market IoT Use Cases”, IEEE Access 2021;
- S. Rappaport et al., “Millimeter wave mobile communications for 5G cellular: It will work!” IEEE Access, 2013.