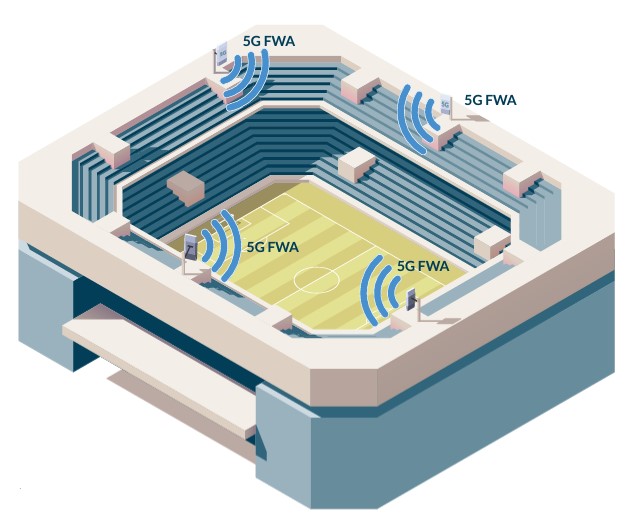
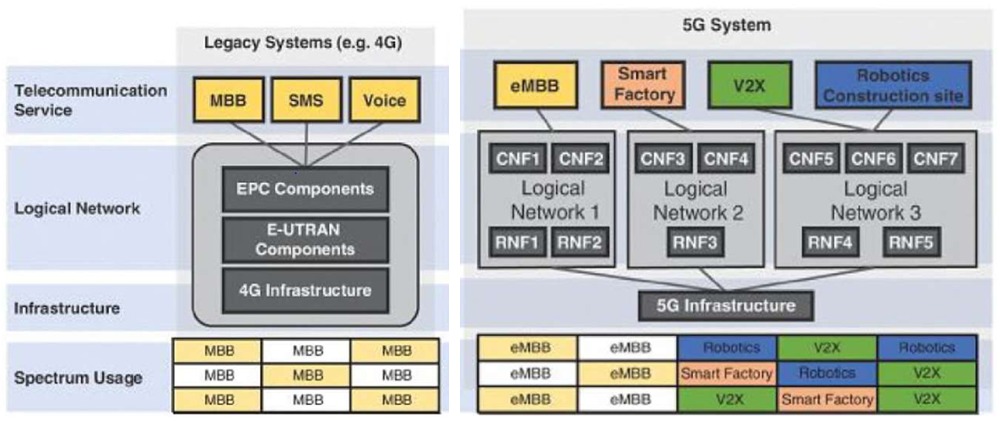
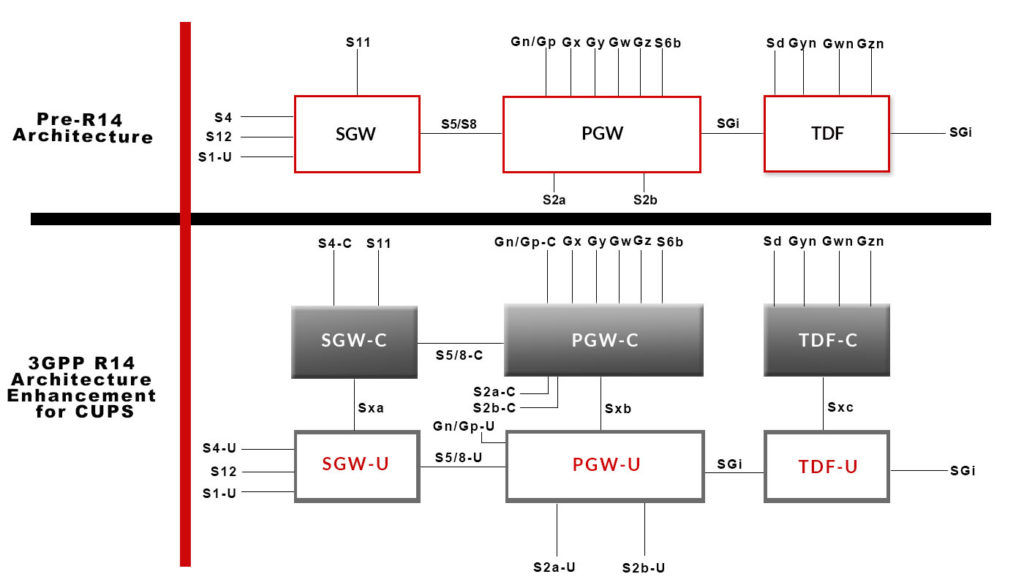
With the rapid development of technology, manufacturers are pushing the market for smart mobile devices to cover the increasing user demands. This rise in traffic results in a tendency to increase the volume of data being transmitted within the communications networks. In conjunction with the Internet of Things, the Operators need to avoid network congestion that creates long delays, impacting the final user experience. It is, therefore, necessary to develop a new generation of 5G networks to meet the ever-increasing needs of users, with the primary objective of achieving the lowest latency and maximum possible performance.
5G networks will be able to support new technologies such as Cloud Computing utilizing network imaging technology as well as an extension of Cloud Computing, Mobile Edge Computing (MEC). Edge Computing does not replace but complements Cloud Computing and is capable of moving content closer to the end-users. Moving content closer will serve their requirements in a faster manner, and, thereby, isolate traffic to the core network while enhancing the overall quality of service.
Cloud Computing definition
A cloud refers to a discrete Information Technology (IT) environment designed to provide scalable and measurable IT resources remotely. The term comes from the Internet, where a network of networks provides remote access to a set of decentralized IT resources.
Cloud computing is currently at the top of the list of strategic telecom solutions. The Cloud platform recognizes the importance of scalability, in terms of the possibility of vertical scaling, that is, the replacement of one IT resource by another with higher or lower capacity.
Cloud Computing Advantages
The benefits of using cloud computing are significant for both end-users and businesses. Companies that offer computing resources offer many features that can benefit customers using cloud technology. Network providers have the appropriate know-how to develop and maintain the infrastructure and environment for development or implementation. The responsibility for the infrastructure lies with providers and not with businesses. Businesses do not have to deal with issues regarding their information systems infrastructure.
Low Cost: When Amazon first launched its cloud services, it offered on-line storage in a data center. Today, it offers more services at much lower prices, as large companies such as Microsoft and Google now offer cloud services to consumers. So from this competition, the end customer and the business benefit because the options provided are continually increasing at a low cost.
Service pricing: Users consume on-demand computing resources by paying according to their usage. Companies pay money from the budget for operating expenses rather than paying for capital expenditures. This makes cloud-based services very attractive to new startups because they can have computing resources that they wouldn’t otherwise have. This approach, namely pay-per-use, attracts small and medium-sized enterprises that cannot afford to invest in complicated and expensive infrastructure. This allows them to purchase only the services they need by paying the relevant price while avoiding high costs that would lead to off-budget.
Flexibility: Service server hire is very flexible in terms of computing resources because companies are given a choice of technology to use. They can decide the exact computing space to use and the corresponding amount of processing power. Even administrators can, in real-time, decide to update software applications by determining how much they will invest in the security of their computing systems. Clouds can meet the changing needs of information systems with great flexibility.
Extensibility: Cloud technology enables users to manage small volumes of data and, if needed, to gain immediate access to large volumes of data in a minimal amount of time. So they can process large amounts of data for a certain period and return to their normal flow of data as soon as that period is over. This solution is more cost-effective for companies that can rent out computing power, at a cost per gigabyte, than buying equipment and sophisticated machinery. Thus, cloud computing allows businesses to quickly adapt to new needs by expanding the capabilities of their information systems.
Fast deployment: In the installation of a new information system, various time-consuming tasks are required, such as specifying, ordering, receiving, installing, setting up, etc. In the cloud, the corresponding infrastructure may start operating in just a few minutes as long as the business case is defined.
Portability/Access from everywhere: Web applications can be accessed from anywhere without the use of VPNs. Cloud computing promises access to high-power computing resources for anyone with an Internet access device that facilitates users’ needs across different time zones and geographic locations. Companies may now compete globally, while work from home may now be introduced, increasing the productivity of employees and their willingness to work.
Unlimited storage: Cloud storage provides virtually unlimited storage, and there is no need for both company and customer concerns of running out of storage.
Diversity of access devices: Cloud computing services can be accessed from a variety of electronic devices such as smart-phones, and tablets in addition to traditional computers. The end-user can specify the equipment and the service that will allow him access to the data. Therefore there is no restriction of place and medium, and this is very attractive to end-users.
Backups and recovery from damage: Cloud computing is usually built on a robust architecture providing Customization and Backup for users. The cloud offers automatic switching between out of the box hardware platforms, together with disaster recovery services.
Environment-friendly: The cloud is environmentally friendly because it uses as much space as the application needs on the server. This kind of scalable usage minimizes overall power consumption.
Using Cloud Computing in 5G Systems
By merging Cloud Computing into the 5G Radio Access Network (RAN), C-RAN is envisioned as the future 5G wireless system architecture. Thanks to the pioneering move of baseband editing feature to a centralized cloud band unit, C-RAN is expected to reduce power consumption significantly, and move a step closer towards a green 5G RAN. In addition, with cloud-based architecture, many new functionalities and RAN designs are ready to be incorporated, which redefine RAN as a flexible RAN.
Centralized Radio Access Network (C-RAN)
In the Cloud Radio Access Network (or C-RAN) architecture, the base station functions are divided into the Remote Radio Unit (RRU) and the Baseband Unit, BBU. The RRU is located on the base station, and the BBU is centralized in a Data Center.
The great advantage of C-RAN compared to conventional RAN in terms of power reduction is the centralized BBU pool. More specifically, from a cloud computing point of view, RAN manages the transitions not only from multiple distributed base stations to a centralized BBU pool but also from a hardware-defined infrastructure to a software-defined environment. This results in computing technology clouds in a centralized BBU pool to push the RAN to be more energy efficient. For example, the cooling system is installed at each base station (BS) in the conventional RAN. However, in C-RAN, the cooling system is installed in the centralized BBU pool. This way, the cooling power can be adapted to the number of active servers, which may be dynamically configured in cloud computing.
On the other hand, the software-defined environment in the BBU pool provides more flexibility in C-RAN. Many new functionalities can be added to C-RAN with software upgrades since processing, control, and management within C-RAN are now all software-based.