Introduction
The relentless pursuit of more robust, efficient, and sophisticated communication systems has led the 3GPP’s advancements from Release 17 to Release 18, marking a pivotal transition in the realm of 5G technologies. Among the various enhancements, Multiple Input Multiple Output (MIMO) and beamforming have been instrumental in achieving the high data rates and network reliability promised by 5G.
However, as we step into the nuances of Release 18, these technologies undergo a transformative upgrade, addressing the complexities and challenges of an increasingly connected world that demands more from its wireless networks.
In Release 17, the focus on MIMO and beamforming was directed towards establishing a solid foundation for enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB) and ultra-reliable low-latency communications (URLLC). These implementations paved the way for a wide array of industrial and consumer applications, pushing the boundaries of what was previously possible with 4G technologies.
Now, with Release 18, we embark on a journey to refine these capabilities further. This release is expected to bring about an evolution in MIMO and beamforming that not only enhances network performance but also expands the horizons of use cases—from smart cities and automated industrial environments to high-speed vehicular networks and beyond.
In this article we will have a look at these enhancements in detail, exploring the impact on network performance, practical applications, and the forward march towards an even more connected future.
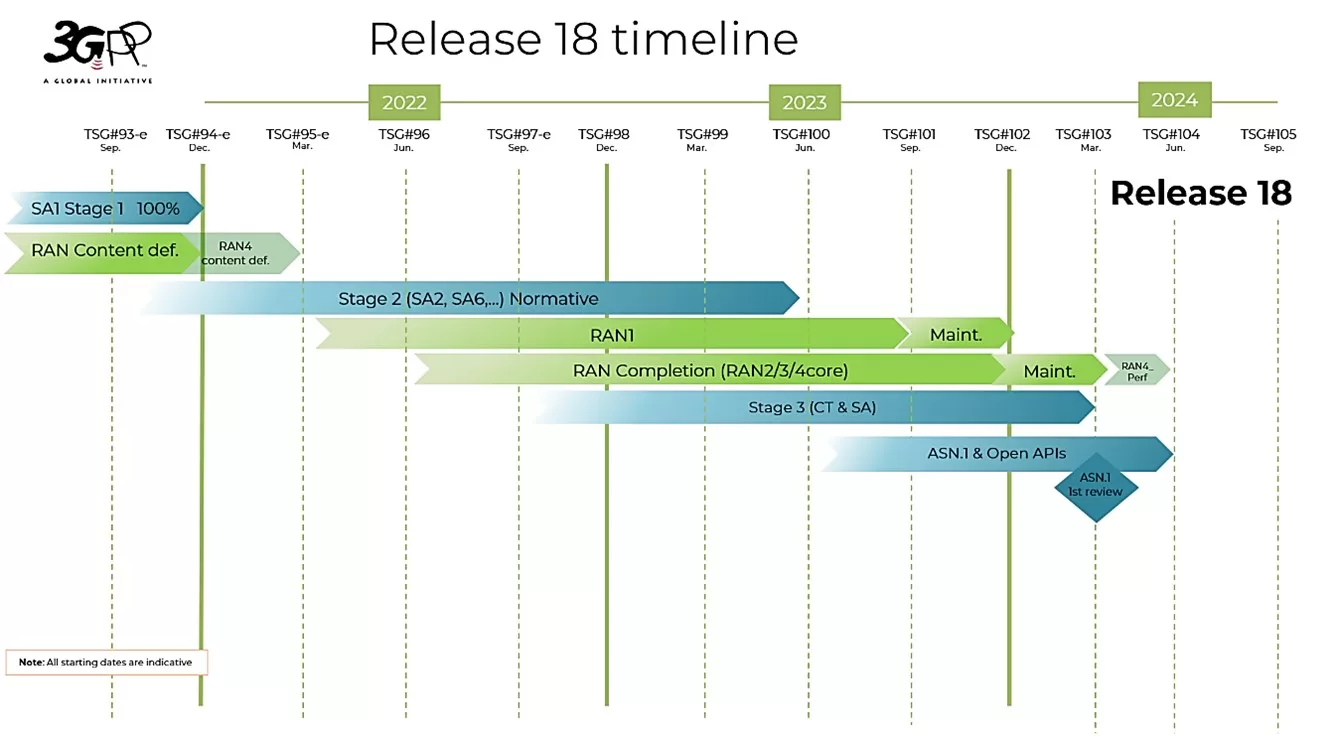
Figure 1: Release 18 timeline
Understanding MIMO and Beamforming in 3GPP Release 17
MIMO and beamforming technologies have been cornerstones in the architecture of 5G networks, as laid out by the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) in Release 17. Their complex interplay has been instrumental in propelling the capacity and efficiency of wireless communication systems.
In Release 17, MIMO technology advanced significantly, with a focus on enhancing the performance of 5G New Radio (NR). This release saw improvements in MIMO’s ability to support a multitude of antennas at both the transmitter and receiver ends. This multi-antenna strategy is essential for meeting the high data throughput and reliability requirements of 5G networks, especially in densely populated urban environments and high-demand industrial settings.
Beamforming, a technique that directs the transmission of radio signals to establish a communication link, underwent refinements to increase network capacity and coverage. The advancements allowed for more precise targeting of radio waves to user equipment (UE), which minimized interference and maximized signal strength. This was particularly beneficial for users on the move, as the technology adapted to changing angles and distances to maintain a strong connection.
Release 17 focused on streamlining the signaling involved in beam management, which reduced latency and improved system performance for high-speed users. Additionally, enhancements were made in supporting mobile devices with multiple antenna panels, thereby improving the signal reception and broadening the coverage area.
The introduction of multi-Transmission and Reception Point (mTRP) operations for both URLLC and eMBB use cases was a key development in Release 17. It enabled robustness in communication, especially where high reliability and low latency were crucial, such as in automated manufacturing processes and autonomous vehicular communications.
Specifically, for URLLC, the improvements in MIMO and beamforming ensured that critical data could be transmitted with minimal delay and the highest possible reliability. In the context of eMBB, these enhancements facilitated the delivery of high-bandwidth content, such as video streaming and virtual reality applications, with greater efficiency and reduced lag.
3GPP Release 17’s enhancements in MIMO and beamforming laid the groundwork for a more sophisticated and capable 5G network. These improvements in multi-antenna techniques have set the stage for subsequent enhancements in Release 18, aiming to unlock even greater potentials of 5G networks and cater to the proliferating demand for connectivity in an ever-more interconnected world.
Technical Enhancements in 3GPP Release 18
3GPP Release 18 is poised to enhance the technical capabilities of 5G networks further, building upon the robust foundation established by the previous standards. This release is expected to introduce several critical enhancements that will augment the efficiency and performance of 5G systems.
Advancements in MIMO Technologies
Release 18 is focusing on advancing MIMO technologies. It aims to extend the boundaries of antenna technology by increasing the number of supported antenna ports. This expansion is expected to enable more intricate beamforming strategies, allowing for improved user capacity and enhanced signal quality in scenarios involving high mobility, such as on high-speed trains.
Refinements in Beamforming Techniques
Beamforming is undergoing significant refinements, particularly in the management of beam-related signaling. The objective is to reduce the signaling overhead linked with beam switching, essential for maintaining seamless user experiences as devices move across the network. Additionally, enhancements in beamforming are targeted at optimizing signal transmission and reception, thereby improving network throughput and coverage.
Integration of AI and ML within Network Fabric
Release 18 plans to explore the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) within the network framework. By utilizing these technologies, the network can intelligently predict and adapt to changing conditions in real-time. This includes dynamically adjusting MIMO configurations and beamforming patterns to optimize network performance autonomously.
Improvements in Network Energy Efficiency
Another focal point of Release 18 is enhancing network energy efficiency. As networks expand and sustainability becomes a crucial focus, techniques to reduce the power consumption of base stations and other network elements are key considerations, likely influencing MIMO and beamforming technologies to operate more efficiently.
Optimizing Spectrum Usage
The release will also continue to enhance the flexibility of spectrum usage. It aims to optimize the use of available spectral resources, improving the capacity and coverage of 5G networks, especially in fragmented and varied frequency bands.
Enhancing Network Topology with IAB
In terms of network topology, there is an expected refinement in the concept of Integrated Access and Backhaul (IAB) and an extension of capabilities in multi-hop backhauling. This is vital for supporting advanced MIMO configurations and ensuring that backhaul links can sustain the high data rates required by these technologies.
Addressing a Diverse Range of Devices
From a device perspective, Release 18 will continue to address the needs of a diverse range of devices, including those not typically categorized as smartphones. Enhancements will likely cater to devices that require less complexity and power but still benefit from advancements in MIMO and beamforming, such as IoT devices and wearables.
Overall, 3GPP Release 18 is expected to be a significant milestone in the evolution of 5G networks, with technical enhancements in MIMO and beamforming, coupled with the integration of AI, and advancements in spectrum efficiency and network architecture, aiming to elevate the performance, capacity, and sustainability of 5G systems.
Case Studies and Practical Applications
The advancements in MIMO and beamforming technologies in 3GPP Release 18 have practical implications across various sectors. This section explores case studies and applications that demonstrate the real-world impact of these technical enhancements.
Urban High-Density Networks
A metropolitan city with high-rise buildings and dense population presents unique challenges for network coverage and capacity. The implementation of advanced MIMO and beamforming technologies in this setting led to significant improvements in network performance.
- Increased Coverage and Capacity: Enhanced beamforming capabilities allowed for more directed signal paths, overcoming urban obstacles like buildings, and reducing dead zones.
- Improved User Experience: Residents and businesses experienced higher data speeds and reduced latency, facilitating better streaming, gaming, and communication services.
Industrial Automation
A large industrial complex with automated machinery and Industrial IoT (IIoT) devices deployed advanced MIMO technologies for seamless connectivity.
- Reliable Low-Latency Communication: The low-latency and high-reliability features supported critical operations like remote control of machinery and real-time data processing.
- Enhanced Device Connectivity: The increased number of connections per cell enabled by advanced MIMO allowed for a greater number of IoT devices to operate simultaneously without congestion.
Public Safety and Emergency Services
A city’s public safety network utilized beamforming advancements to improve communication during emergencies.
- Focused Signal Transmission: Beamforming ensured reliable and clear communication for first responders, even in areas with traditionally poor coverage.
- Rapid Deployment: Portable cell stations with enhanced MIMO capabilities were deployed during large public events, offering improved capacity and coverage.
Automotive and V2X Communication
An urban area tested vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication using the enhanced MIMO technology.
- Cars were able to maintain consistent and reliable connections with each other and roadside infrastructure, enhancing safety features like collision avoidance.
- The low latency and high data rate capabilities facilitated the testing and development of autonomous vehicle technologies.
These case studies exemplify the transformative potential of the MIMO and beamforming enhancements in 3GPP Release 18. From dense urban environments to industrial applications and public safety, the improvements in network performance, capacity, and coverage have wide-reaching impacts, paving the way for innovative uses of 5G technology.
Challenges and Considerations in Implementing MIMO and Beamforming Enhancements
The transition from 3GPP Release 17 to Release 18, with its focus on MIMO and beamforming enhancements, presents several challenges and considerations. Let’s have a look and addresses the technical and practical aspects that stakeholders need to navigate to effectively leverage these advancements.
Figure 2: Challenges and Considerations in Implementing MIMO and Beamforming Enhancements
Hardware Upgrades and Cost Implications One of the primary considerations is the need for equipment upgrades. Implementing advanced MIMO and beamforming technologies often necessitates upgrading existing network hardware, including antennas and base stations. This leads to significant cost considerations, as these upgrades can be capital intensive, especially when deployed across large networks. This necessitates careful budgeting and investment strategies.
Technical Complexity in Deployment The deployment of advanced MIMO systems involves complex configurations and tuning to optimize performance, requiring specialized expertise. Additionally, integrating new MIMO and beamforming technologies with existing network infrastructure presents challenges, particularly in environments where multiple generations of network technology coexist.
Spectrum Management Effective use of advanced MIMO and beamforming relies heavily on the availability of appropriate spectrum bands, which can be limited or subject to regulatory constraints. Additionally, with the increased signal directivity and multiple beams that these technologies bring, managing interference, especially in dense network deployments, becomes more crucial.
Environmental and Health Concerns Another area of concern is the environmental impact, as higher MIMO orders and more sophisticated beamforming techniques can lead to increased energy consumption. Alongside environmental impacts, ongoing monitoring and compliance with health and safety standards related to electromagnetic exposure remain important, considering the evolving nature of network technologies.
User Equipment (UE) Compatibility The full benefits of enhanced MIMO and beamforming can only be realized if user devices are equipped to support these advanced features. Therefore, device readiness and market adoption are crucial. This involves not only the availability of such devices but also their affordability for consumers.
Scalability and Future-Proofing Network designs must be scalable to accommodate future growth in user numbers and data demand. Moreover, as wireless technologies continue to evolve, ensuring that current enhancements are forward-compatible with future standards is key to their long-term viability.
In conclusion, while the MIMO and beamforming upgrades in 3GPP Release 18 offer substantial benefits, they also bring a set of challenges that need to be carefully managed. Stakeholders must navigate these complexities to fully harness the potential of these advanced wireless communication technologies.
References
- 3GPP Work Plan #231006 – Rel-18
- 3GPP TS 23.041 version 18.0.0 Release 18
- Jin et al., “Massive MIMO Evolution Toward 3GPP Release 18,” in IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, vol. 41, no. 6, pp. 1635-1654, June 2023, doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2023.3273768.
- Lin, “An Overview of 5G Advanced Evolution in 3GPP Release 18,” in IEEE Communications Standards Magazine, vol. 6, no. 3, pp. 77-83, September 2022, doi: 10.1109/MCOMSTD.0001.2200001.

