Introduction
The world of supply chain and inventory management is changing fast, and the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is at the center of this transformation. In simpler terms, IIoT is all about connecting machines and devices in industries to collect and share data in real-time. It’s taking us from the old days of having to manually check and manage inventory to a new age where much of this work is automated, data-driven, and happening in real-time.
Today, if you’re running a business, it’s more crucial than ever to have the right items, in the right place, at the right time. It sounds straightforward, but anyone in the industry knows it’s anything but. That’s where IIoT comes in. With it, managers can track products and materials in real time as they move from manufacturers to warehouses to retail locations. This doesn’t just save time; it also significantly reduces errors and costs, ensuring businesses can meet customer demands efficiently.
In this article, we’re going to take a deep dive into the specifics of how IIoT is reshaping supply chain and inventory management. We’ll explore real-world applications, the benefits and challenges, and what the future might hold for businesses ready to step into this new era of enhanced visibility and control.
The Challenges in Contemporary Supply Chains
Every industry faces its set of hurdles, and supply chain management is no exception. In the modern, highly competitive business landscape, the supply chain is often where companies encounter a slew of challenges that can impact efficiency and profitability. Let’s break down some of the most common issues.
Visibility Issues
One of the fundamental challenges is visibility, or rather, the lack of it. Traditional supply chains often involve manual processes and disconnected systems, leading to gaps in the visibility of goods as they move through various stages. Without a clear, real-time view of the inventory, businesses can struggle to make informed decisions, leading to overstocking, stockouts, or delays.
Demand Forecasting
Accurately predicting customer demand is another significant hurdle. With consumer trends changing rapidly, businesses often find it difficult to forecast demand accurately. Misjudging the market need can lead to excessive inventory costs or missed sales opportunities.
Operational Inefficiencies
Operational inefficiency is a classic challenge. Outdated processes, manual handling, and a lack of automation can lead to errors, wasted time, and increased operational costs. The speed and accuracy at which the inventory moves between manufacturer and consumer are critical factors in determining a business’s success.
Security and Compliance
In the era of globalization, supply chains are sprawling and complex. With this complexity comes increased vulnerability to theft, tampering, and counterfeiting. Additionally, adhering to the varied regulatory requirements across different regions can be a complicated and often costly affair.
Integration Issues
As businesses grow, integrating new technologies or processes with existing systems can be a daunting task. Siloed data and applications can hinder the seamless flow of information across the supply chain, affecting real-time decision-making.
In the following sections, we will explore how IIoT technologies are addressing these challenges, offering solutions that not only mitigate these issues but also enhance the overall efficiency and responsiveness of the supply chain.
Understanding IIoT’s Role
In today’s multifaceted supply chain ecosystem, the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is progressively becoming integral. It facilitates the evolution of traditional supply chains into adaptable, responsive systems capable of managing variable demands and unforeseen challenges efficiently.
The utility of IIoT is largely attributed to its capability to provide real-time visibility throughout the supply chain. Enabled by sensors and advanced networking technology, IIoT devices can effectively track and monitor products from manufacturing, warehousing, in transit, to the retail shelf. Consequently, a continuous stream of real-time data is made available, aiding decision-makers in optimizing inventory levels, reducing lead times, and promptly addressing emerging issues.
Through the analysis of data collected by sensors and RFID tags, Industrial IoT (IIoT) enhances supply chain visibility. For example, by examining data from RFID tags on inventory items and sensors within a smart warehouse, a supply chain management system delivers real-time information to warehouse staff regarding item location, status, and condition. It also offers notifications on incoming deliveries and insights into warehouse equipment usage.
To facilitate seamless data sharing, IIoT solutions integrate with other enterprise systems such as Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES), Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), Warehouse Management Systems (WMS), Process Information Management Systems (PIMS), and Distributed Control Systems (DCS). For instance, an IIoT solution can access maintenance department data to ensure the condition of shipping vehicles or provide the accounting department with real-time asset data required for annual reports.
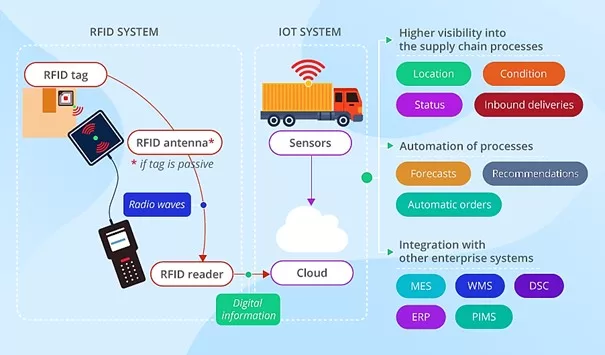
Figure 1: System Model of IIoT in Supply Chain
IIoT also plays a crucial role in enhancing the security of the supply chain. With features like real-time tracking and monitoring, businesses can quickly identify and respond to security breaches. Additionally, IIoT devices can be programmed to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements, automating tasks like reporting and auditing to simplify compliance.
Key Applications of IIoT in Supply Chain Management
The integration of IIoT within supply chain operations is not just a trend but a significant leap towards enhanced efficiency, transparency, and productivity. By focusing on real-world applications, we can uncover the transformative impact of IIoT. Here are some key areas where IIoT is making a tangible difference.

Figure 2: Key Application of IIoT in Supply Chain Management
- Inventory Monitoring and Optimization
IIoT sensors and devices installed in warehouses collect real-time data on inventory levels, conditions, and locations. This real-time data helps businesses maintain optimal inventory levels, reducing the costs associated with overstocking or stockouts. For instance, smart shelves in warehouses can send alerts when it’s time to restock, ensuring that popular products are always available.
- Predictive Maintenance
With IIoT, machinery and equipment in the supply chain are equipped with sensors that monitor their condition in real-time. Predictive algorithms analyze this data to anticipate when maintenance is required. This approach prevents unexpected breakdowns, reducing downtime, and maintenance costs. For example, sensors on a conveyor belt can detect wear and tear, scheduling maintenance before a breakdown occurs.
- Real-Time Tracking and Visibility
GPS and RFID technologies powered by IIoT enable real-time tracking of goods as they move through the supply chain. This enhanced visibility ensures timely deliveries, allows for dynamic routing to avoid delays, and provides customers with real-time updates on their orders. For instance, a retailer can track a shipment of goods and adjust store staffing levels based on the anticipated arrival time.
- Enhanced Quality Control
IIoT devices can monitor the conditions of products throughout the supply chain, especially crucial for perishable goods. Sensors can track temperature, humidity, and other environmental factors, ensuring products are stored and transported under optimal conditions. In the pharmaceutical industry, for example, IIoT ensures that temperature-sensitive drugs are stored and transported within the required conditions, maintaining their efficacy.
- Automated Reporting and Analytics
The vast amount of data generated by IIoT devices provides invaluable insights for decision-making. Automated reporting tools can process this data to produce actionable insights, improving decision-making and forecasting. In a scenario where a retailer is launching a new product, IIoT data can help predict the demand, influencing production, stocking, and marketing strategies.
- Enhanced Security
Security is paramount in supply chain operations. IIoT enhances security protocols by offering real-time monitoring and alerts for any unauthorized access or anomalies. For high-value goods, sensors can detect and alert managers to any unexpected movements or environmental changes, prompting immediate action.
- Regulatory Compliance
IIoT aids in meeting the stringent regulatory requirements in the supply chain by automating the collection and reporting of compliance data. For food and beverage companies, for instance, IIoT ensures that products are stored and transported within regulatory guidelines, automating documentation and reporting processes for regulatory submissions.
In conclusion, IIoT is transforming supply chain management by offering solutions that are not only efficient but also adaptive to the changing demands and challenges of the modern market. In the subsequent sections, we’ll explore case studies to illustrate the tangible benefits and ROI businesses are experiencing from integrating IIoT into their supply chains.
The Future of Supply Chains with IIoT
The evolution of the supply chain is inextricably linked with the advancements in technology. As we peer into the future, it’s clear that IIoT will play a significant role in redefining how we understand and manage supply chains. Here, we outline some of the trends and projections that could characterize the future of supply chains enhanced by IIoT.
In the future, supply chains powered by IIoT will boast real-time monitoring and decision-making. Every element, from inventory levels to the condition of goods, will be tracked, analyzed, and responded to in real time. This will lead to enhanced responsiveness, allowing companies to adapt to changes in the market instantly, reducing lead times and out-of-stock scenarios.
As IIoT continues to mature, the analytics tools that companies use to interpret and act on data will also evolve. We will see a move towards predictive and prescriptive analytics, where AI algorithms not only predict future trends but also recommend actions to optimize supply chain performance. This will enable companies to be proactive rather than reactive, addressing potential issues before they escalate.
Automation will move beyond the warehouse and transportation management to encompass every aspect of the supply chain. IIoT will facilitate the integration of automation technologies, leading to more streamlined, efficient, and error-free operations. From automated order processing to AI-driven demand forecasting, the supply chain will become faster and more reliable.
With the interoperability features of IIoT, different elements of the supply chain, including suppliers, manufacturers, and retailers, will be able to share data seamlessly. This enhanced collaboration will lead to more cohesive and efficient supply chains, where partners can align their operations to achieve common objectives, fostering an ecosystem of innovation and efficiency.
As environmental concerns continue to influence business strategies, IIoT will be instrumental in promoting sustainable practices within the supply chain. Enhanced data and analytics will enable companies to monitor and reduce their carbon footprint, optimize energy usage, and minimize waste, aligning operations with global sustainability goals.
Challenges in the Implementation
The integration of IIoT in supply chain management is a double-edged sword. While it offers a multitude of benefits, companies must also navigate some important challenges.
Data Security and Privacy
As IIoT involves the collection and exchange of massive amounts of data, ensuring the security and privacy of this data is paramount. Companies must implement robust cybersecurity measures to protect sensitive information from breaches and unauthorized access.
Cost of Implementation
The initial investment required to integrate IIoT into supply chain operations can be substantial. Companies need to consider the costs associated with purchasing technologies, training staff, and maintaining and upgrading systems.
Merging IIoT with Existing Systems
Incorporating IIoT into existing infrastructures is more about enhancing what’s already in place than starting anew. It involves a delicate dance of integrating cutting-edge IIoT devices with older systems from various manufacturers, each with its unique language of data and operation.
Tech teams often navigate this complex mix, where no established playbook exists yet, especially in an industry still carving out its standards. The challenge amplifies when dealing with a flood of diverse data produced by a combination of old and new technologies.
In this scenario, integrating IIoT becomes an intricate dance of technology and a symphony of diverse data, promising a harmonized world of innovation and enhanced value.
Conclusion
Through this article we’ve seen how the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is revolutionizing supply chain and inventory management. It highlights the challenges faced in contemporary supply chains, including visibility issues, demand forecasting, operational inefficiencies, security, and integration problems. IIoT’s role in addressing these challenges is discussed, with a focus on real-world applications such as inventory monitoring, predictive maintenance, real-time tracking, quality control, automated reporting, enhanced security, and regulatory compliance.
The future of supply chains with IIoT is described, emphasizing real-time monitoring, advanced analytics, hyper-automation, enhanced collaboration, sustainability, and customization. We’ve come to see the challenges of implementing IIoT, including data security, the cost of implementation, and the complexity of merging IIoT with existing systems.
We can assume that IIoT offers significant benefits for supply chain management but comes with challenges that must be navigated.
References
- Kayapinar Kaya, Sema. (2020). How Industrial Internet of Things Impacts on the Supply Chain. 10.4018/978-1-7998-3175-4.
- https://www.ericsson.com/en/blog/2022/5/how-iot-in-the-supply-chain-can-help-manufacturers
- “Connected Supply Chain: Top Questions Answered”, Serge Legchekov, https://www.scnsoft.com/blog/

