Introduction
In the realm of wireless communication and digital devices, the marriage between the Internet of Things (IoT) and evolving cellular technologies has sparked a revolution. Each day, a plethora of devices—smart thermostats, wearable health trackers, industrial sensors, and more—come online, requiring seamless connectivity and robust networks to function efficiently. However, as these devices grow in complexity and number, the foundational elements that empower them, like the Subscriber Identity Module (SIM), have needed to evolve in tandem.
Enter the era of the eSIM—Embedded Subscriber Identity Module—a progressive step from the physical SIM cards of yore. In the shimmering dawn of 5G, a technology promising unmatched speeds, unparalleled connectivity, and undreamt-of applications, the eSIM emerges as a crucial player. This compact, reprogrammable module doesn’t just simplify device manufacturing and deployment; it’s also heralding a future where devices seamlessly interact on a global scale, devoid of the restrictions imposed by traditional SIMs.
This article seeks to journey through the evolution of eSIM, particularly under the luminous spotlight of 5G, exploring its significance, advantages, and transformative impact on IoT deployments.
Background: Understanding eSIM
For decades, the physical SIM card was central to mobile devices, providing secure access to networks and storing crucial user data. However, the emergence of smart devices and IoT signaled a need for evolution. Enter the eSIM, or Embedded Subscriber Identity Module. Unlike traditional removable SIM cards, eSIMs are digital and embedded directly into devices, offering the ability to activate cellular plans without physical intervention. They can be remotely reprogrammed, allowing for unparalleled flexibility, especially for devices where swapping a physical card is challenging. Furthermore, eSIMs adapt seamlessly across global networks, ensuring devices can function effortlessly in diverse regions. Initially introduced by GSMA in the early 2010s, eSIMs have gained traction with manufacturers recognizing their convenience. As we transition deeper into the 5G era, the importance of eSIMs only magnifies, underscoring a shift from tangible cards to dynamic, embedded solutions.

Figure 1: Evolution of SIM
Why eSIM is Central in a 5G World?
With the IoT landscape growing exponentially and 5G promising to elevate its capabilities, the role of eSIM becomes more pronounced. Offering unparalleled flexibility and scalability, eSIM is poised to be a linchpin in ensuring the success of 5G-driven IoT deployments.
- Simplified Device Onboarding: As industries and cities become smarter, the sheer volume of devices needing network access will grow exponentially. eSIM makes the onboarding process seamless, quick, and efficient.
- Global Roaming and Interoperability: With 5G, the dream of globally connected devices becomes a reality. eSIM facilitates this by ensuring devices can effortlessly operate across various 5G networks around the world.
- Adaptive Bandwidth Management: eSIM’s dynamic profile management is especially beneficial in a 5G setting, where bandwidth requirements can vary drastically based on the application.
- Enhanced Security Protocols: eSIMs come with robust encryption and security features, ensuring the vast amounts of data generated in a 5G environment are securely transmitted and stored.
- Remote Management: Should a security concern arise, eSIMs can be remotely managed, updated, or even locked down, offering an additional layer of protection in the expansive 5G IoT ecosystem.
The sector recognizes the significant advantages of eSIM technology, while also acknowledging a few surmountable challenges. eSIM enables numerous connection profiles on a single device, even those that haven’t been connected before. This paves the way for simpler network transitions, heightened security, and space conservation. As a survey participant highlighted, “eSIMs eliminate constraints. They offer our corporate clients the freedom to explore and implement extensive IoT solutions by facilitating remote operator changes.” This points towards a superior customer journey, with instantaneous service provisions, allowing companies to spearhead digital transformation, unearth new use cases, and find fresh revenue streams.
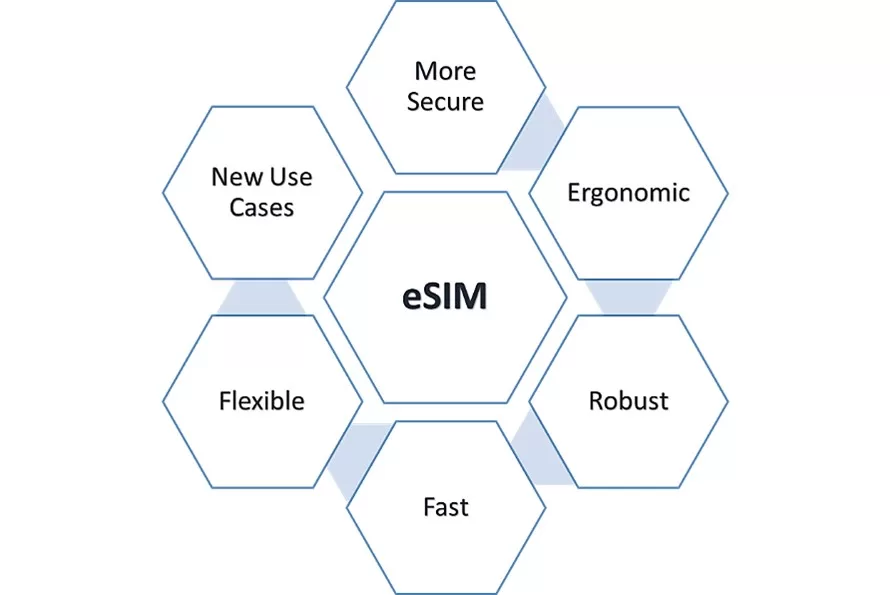
Figure 2: eSIM Advantages
Survey data indicates that eSIM is gaining traction as a trusted, feasible solution for cellular and low-power wide-area (LPWA) connections. A significant 80% of survey participants anticipate eSIM to be the primary authentication method for virtually all eSIM-equipped devices within the next two years.
An Optimistic Outlook on Rapid eSIM Integration The sector is exuberant about the rapid adoption trajectory of eSIM technology, expressing full commitment to its accelerated progression.
Real-world Use Cases: eSIM in Action
The theoretical advantages of eSIM in 5G IoT deployments are undeniably compelling. Yet, its true potential shines through in real-world applications where the fusion of eSIM and 5G is already transforming industries and redefining what’s possible. Let’s dive into some real-life scenarios where eSIM is making a tangible difference.
Global Fleet Management
- Scenario: A logistics company operates a fleet of trucks that traverse multiple countries, delivering goods across borders.
- eSIM Impact: With eSIM, each truck can seamlessly switch between network providers as they move from one country to another. This ensures uninterrupted GPS tracking, real-time communication, and efficient route optimization based on live traffic and weather data, all without manual SIM swaps or multiple devices.
Wearable Health Devices
- Scenario: A health-tech company produces wearable devices that monitor vital stats in real-time for patients with chronic illnesses.
- eSIM Impact: With eSIM and 5G, these wearables can transmit data continuously to healthcare providers regardless of the patient’s location. This ensures prompt emergency responses and allows medical professionals to adjust treatments based on real-time data.
These real-world scenarios underscore the transformative potential of eSIM in 5G IoT deployments. It’s evident that as industries evolve and as the 5G landscape expands, the role of eSIM will only become more pivotal, acting as the bridge connecting devices, data, and dynamic decision-making.
The Future of eSIM in a Post-5G World
As we stand on the brink of a new telecommunications era, the union of eSIM and 5G has already started reshaping the contours of connectivity. However, technology doesn’t stagnate; it evolves. As we look beyond 5G towards 6G and other advancements on the horizon, what role will eSIM play?
- Expansion in Consumer Electronics
Beyond IoT, eSIM will become a staple in everyday consumer electronics, from smartphones and wearables to smart home devices.
With devices no longer tied to a particular carrier or region, consumers will enjoy unprecedented flexibility, potentially revolutionizing the telecommunications market dynamics.
- Integrating AI and Machine Learning
As Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning become more entrenched in our digital ecosystem, eSIM systems will leverage these technologies for automated network selections, predictive maintenance, and optimized data usage.
Devices will make intelligent decisions on which network to connect to, based on factors like signal strength, cost, and specific application requirements, without any manual intervention.
- Sustainable and Green Telecommunications
The environmental impact of technology will become a paramount concern. eSIM, being a virtual solution, will lead the way in reducing electronic waste, as the need for physical SIM cards and associated packaging diminishes.
Companies adopting eSIM can highlight their commitment to sustainability, aligning with global green initiatives and appealing to environmentally conscious consumers.
- Proliferation in Emerging and Remote Areas
eSIM, coupled with satellite-based 5G (and eventually 6G), will usher in unparalleled connectivity in remote and historically underserved areas. This will bridge the global digital divide, spurring socio-economic growth in regions previously limited by connectivity challenges.
The future envisions a world where eSIM isn’t just an enabler but a driver, propelling us into a seamlessly connected, intelligent, and sustainable digital age.
Conclusion
The wireless communication landscape is on the cusp of a transformative era, and at its core is the dynamic synergy between eSIM and 5G technology. From its roots as a simple SIM card to its current avatar as the embedded eSIM, this component has constantly evolved to match the growing complexity and needs of IoT devices. Beyond facilitating smoother device manufacturing and global interoperability, eSIM promises to simplify global fleet management, enhance wearable health tech, and more. But its journey doesn’t stop with 5G. As we peer into the future, eSIM is poised to intertwine with consumer electronics, leverage AI for smarter connectivity, champion green telecommunication initiatives, and bridge digital gaps in remote regions. Indeed, as technologies like 6G beckon, the eSIM stands not just as a testament to digital progress but as a beacon for the sustainable, intelligent, and interconnected world that lies ahead.
References
- Remote SIM Provisioning for Machine to Machine: GSMA site posting most of the information.
- [TS 31.102] Characteristics of the Universal Subscriber Identity Module (USIM) application.

