Many years ago, if an organization/Company/factory wanted to deploy a private wireless network at the office building, transit hub, another facility, or over a utility service or other geographic area, its options were limited to Wi-Fi or proprietary network technologies like LoRa or Sigfox.
These legacy private networks were enough for connecting laptops to the Internet. However, the coverage and security limitations of these networks, their incompatibility with public cellular networks, as well as their high ongoing management costs, made it difficult for organizations to use these networks for many IIoT (Industrial IoT)applications.
Recently, a new type of private network – private cellular networks that use 4G Long Term Evolution (LTE) and 5G technologies – have begun to be deployed by many companies.
What are Private 5G networks?
The concept of a private cellular network is not particularly new, as such networks first started using 4G LTE technology in some countries in industries such as mining, emergency services, and defense. But hand-in-hand with the increasing deployment of 5G networks, the concept of a private 5G network is gaining traction in many parts of the world as regulators are increasingly offering enterprises the opportunity to purchase their own 5G spectrum and deploy their own mobile networks, and this is becoming particularly popular in places such as Japan and Germany.
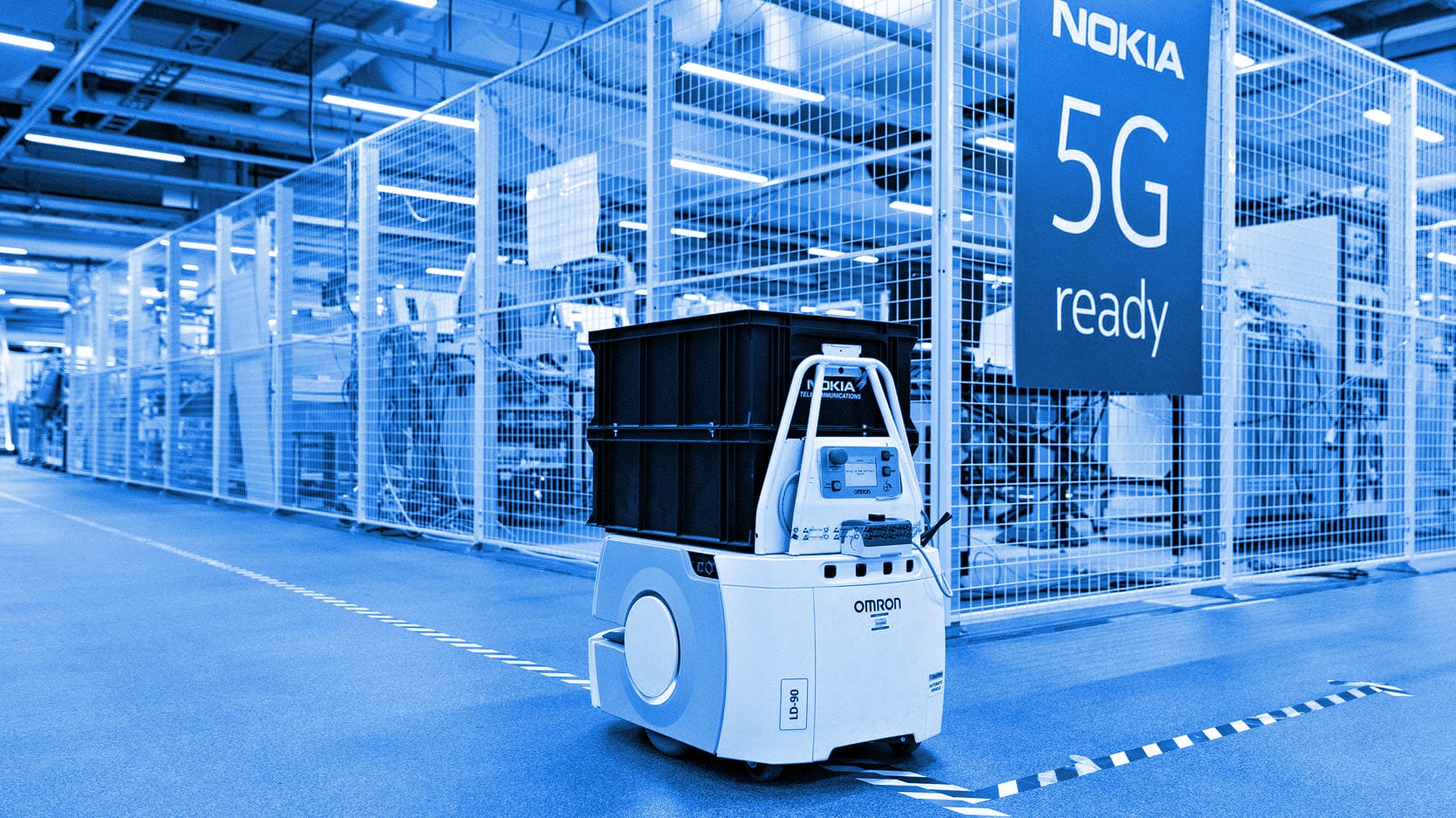

5G Private Network, Image by Nokia
Private 5G networks (referred to as “non-public networks” by 3GPP) are networks that use licensed, shared, or unlicensed wireless spectrum and 5G cellular networking base stations, small cells, and other Radio Access Network (RAN) infrastructure to transmit voice and data to edge devices, including smartphones, embedded modules, routers, and gateways.
“5G private networks can serve the connectivity needs of a broad array of enterprise and industry verticals with high network availability, reliability, and data security for business assurance,” said Xiaoxia Zhang, Senior Director, technology, Qualcomm Technologies, Inc.
To enable enterprise ultra-reliable, high-speed, low-latency, power-efficient, high-density wireless connectivity—a company likely has two basic options.
- It can connect to a public 5G network.
- It can opt for a private 5G network, either by purchasing its own infrastructure while contracting for operational support from a mobile operator or by building and maintaining its own 5G network using its own spectrum.
For many of the world’s largest businesses, Private 5G will likely become the preferred choice, especially for industrial environments such as manufacturing plants, logistics centers, and ports.
Why Private 5G Networks?
Private 5G networks offer considerably more robust security offerings as they need not be connected to the larger telecom network. Hence, they are attractive to companies with very high-security requirements such as power plants.
Private 5G networks are also highly customizable and hence can be built to exact company specifications as opposed to having to select from telco offerings, and data can be managed and analyzed internally. Given that overall 5G rollouts will take time to offer truly nationwide service, especially indoors, private networks can also deliver robust connectivity, meaning customers will no longer have to wait.
Private 5G Networks empower business success, as business data demands increase, dedicated private networks with ultra-reliable, high capacity, low latency 5G and edge computing will empower the enterprise to:
- Enhance network coverage by tapping into increased performance and reduced latency.
- Take control of data and analytics and enhanced data security.
- Improve network costs and efficiency via an agile and scalable architecture.
Unlike a public network, a private 5G network can be configured to a location’s specific needs, and configurations can vary by site, depending on the type of work undertaken in each venue. A private network also allows companies to determine the network’s deployment timetable and coverage quality.
The network may be installed and maintained by onsite personnel, enabling faster responses to issues. Security can be higher, affording network owners a degree of control that may not be possible on a public network: The company determines which users connect, and data can be contained within the site. Keeping data onsite can reduce latency as well. The private network may even run on a dedicated spectrum, reducing the risk of variable service levels due to usage by third parties.
How do Private 5G networks work?
Private 5G networks work the same as public 5G networks operated by Mobile Network Operators (MNOs). Edge devices use a wireless spectrum to transmit data to nearby cellular base stations, access points, and other network infrastructure. The infrastructure then carries this data to the enterprise’s internal network over a secured wired connection. Using this secured connection, data from the edge devices can be sent to various cloud services and applications. To transmit data back to the edge devices, the same process happens in reverse.
The difference between public and private 5G networks resides in who has a license or priority access to the wireless spectrum, and who owns and operates the network’s base stations and infrastructure.
With public 5G networks, the MNO owns and operates the spectrum and the network infrastructure. In addition, generally, all of the MNO’s customers have the same access rights to the network. However, with private 5G networks, private organizations own, operate, or have some level of priority access to the network’s infrastructure or spectrum. The amount of network infrastructure and spectrum owned and operated can vary greatly.
With Full Private 5G networks (which we will focus on in this blog) the organization owns the wireless spectrum it uses for the network, as well as the network base stations and other infrastructure. This provides it with full control over the network and allows it to completely isolate its users from other MNO public networks.
Private 5G Network Sectors
There has been increasing momentum in the private 5G network sector in a variety of industries. Some of the most notable examples include:
-
Private 5G Networks in Manufacturing, Manufacturing is one of the key sectors where private 5G networks are gaining traction as many companies are looking to construct their own networks in order to take the concept of Industry 4.0 to the next level.
Mercedes-Benz is one of the large automotive manufacturers looking to do this and has in fact been working with German telco Telefonica/O2 in order to realize its private 5G network ambitions as part of a greater mission to continue to promote Digital Transformation within its operations. -
Private 5G Networks in Healthcare, One of the fastest-growing areas for private networks in the healthcare space, particularly as the COVID-19 pandemic has recently put incredible strain on the medical infrastructure of many countries.
One such example of a private network being used by a hospital even before the COVID-19 pandemic can be found at the Rush Medical Center in Chicago in the United States. Back in 2019, the facility started to deploy a private wireless network that has gradually incorporated 5G technology. The initial rationale for incorporating 5G was based on their desire to remove the need for physical cables in its buildings which are very expensive to replace. - Private 5G Networks in industrial end-devices like automated guided vehicles (AGV), Qualcomm, and Siemens have setup a joint proof-of-concept project at the Siemens Automotive Test Center in Nuremberg, Germany, demonstrating the first private 5G standalone (SA) network in a real industrial environment using the 3.7-3.8GHz band. Qualcomm Technologies is providing the 5G test network and 5G industrial test devices that run on our foundational 5G technologies, and Siemens is supplying industrial end-devices like automated guided vehicles (AGV).
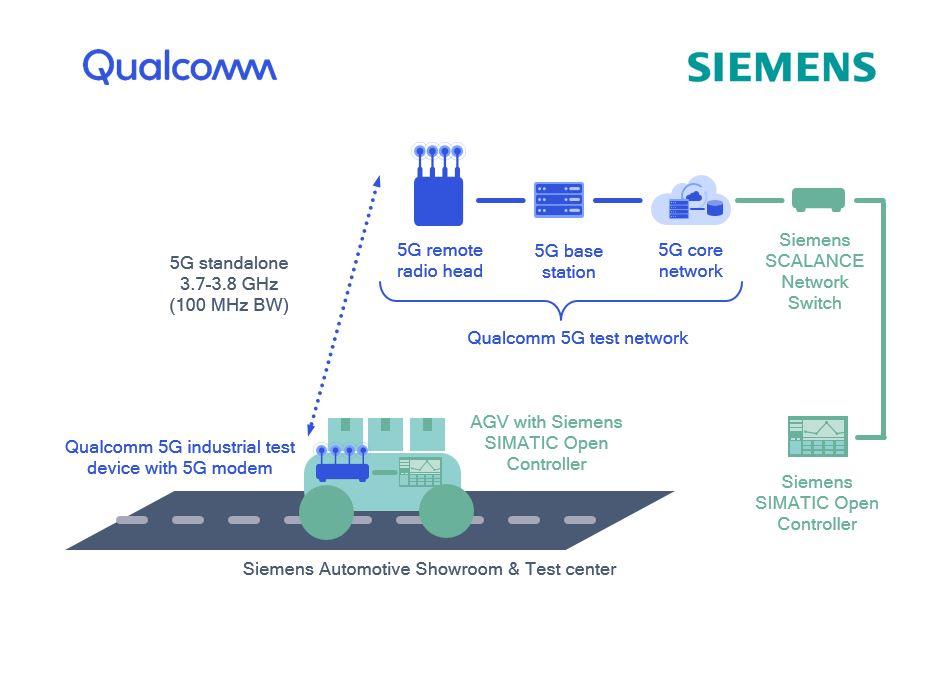
Siemens AGV with Qualcomm Technologies 5G Modem-RF System
References:
- The Growing Case for Private 5G Networks, NEC.
- Mobile network of the future. The world’s first 5G network for automobile production, Daimler.
- Private 5G Networks, Intel.
- Why private 5G networks are on the rise, HPE.
- Private 5G set to transform secure on-site connectivity, Ericsson.
