Introduction
Massive IoT is the deployment of a huge amount of low-complexity devices that do not need to communicate with high frequency. High Performance and low transmission latency are not a requirement.
NB-IoT (narrowband IoT) and Cat-M1, which are both 3GPP standardized technologies develop a Massive IoT strategy. They are very complementary to each other and addressing different types of use cases based on the strength of the capabilities of the two technologies.
The difference between NB-IoT and LTE-M capabilities
LTE-M and NB-IoT are two new technologies for low bandwidth cellular communication. Although these are both low bandwidth technologies, there are important differences to decide when choosing the right cellular protocol for your industrial IoT applications.
NB-IoT
It supports very narrow bandwidth, 200 kHz, So the data rate peaks at around 250 Kbps. Also, it can be deployed even in guard-band of an LTE carrier to use the spectrum that is otherwise unused. You can find more details about What is NB-IOT from here.
LTE-M
LTE-M is considered as the second generation of LTE chips created for IoT applications. It provides low-cost LTE devices suitable for Massive Machine-Type Communications (MTC) and the Internet of Things (IoT) with enhanced coverage compared to normal LTE devices.
There are three main features to focus on when talking about LTE-M:
1. UL Speed and DL speed: Up to 1 Mbps which is quite more than NB-IoT.
2. VoLTE: This technology supports voice service.
3. Mobility: LTE‑M is ideal for mobile use cases.
It operates at 1.4 MHz bandwidth with higher device complexity/cost than NB-IoT. The more bandwidth allows Cat-M1 to achieve data rates (up to 1 Mbps), lower latency and more accurate positioning capabilities. LTE-M supports voice calls and connected mode mobility.
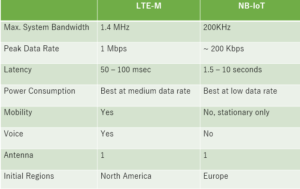
NB-IOT Vs. LTE-M
The Similarities between NB-IoT and Cat-M1 capabilities
Both NB-IoT and Cat-M1 devices can sleep for extended periods of time with extended Discontinuous Reception (eDRX) and Power Saving Mode (PSM) functionalities, which greatly reduces device power consumption. Furthermore, both technologies support enhanced signal coverage per base station.
Which is better, NB-IoT or LTE-M?
Given that LTE-M is more powerful than NB-IoT, that doesn’t mean it’s better. It’s based on the use case, As an example from an operator perspective, NB-IoT can create more deployment flexibility due to guard-band deployment. If the operator’s available frequency assets allow, NB-IoT can also be deployed as stand-alone access.
On the other hand, for IoT applications requiring higher data rates, low latency, full mobility, and voice in typical coverage situations, LTE-M is the best LPWA technology choice.
Resources:
- Ericsson.
- GSMA.