Introduction
As the digital communication of the devices and products is becoming now part of our daily lives, So we need to connect what can make sense to be connected from the home appliances, vehicle devices to the factory and enterprise sector tools.
This connectivity should be secure, reliable and not load the traditional LTE mobile network. So we need NB-IoT.
What is NB-IoT?
At Release 13, 3GPP introduced a new radio interface is called NB-IOT or Narrow Band Internet of Things. It is considered as an optimized version of machine type traffic but with a simple design to reduce device costs and to minimize battery consumption. Also, NB-IoT is adapted to work in difficult radio conditions which are a normal operational area for certain machine type communication devices.
NB-IoT is an independent cellular radio interface to target the low power wide area connectivity market.
Why NB-IoT?
NB-IoT addresses the IoT requirements like improving indoor coverage, supporting the massive number of low throughput devices, low delay sensitivity, low device cost, low device power consumption, and optimized network architecture.

Source: Deutsche Telekom
So NB-IoT helps the MNOs to meed the needs of their customers with low-cost devices. It also will help in many applications like the surveillance cameras which deliver a huge amount of uplink data while being almost stationary and also meter reading devices like electricity, gas or water consumption.
So NB-IoT can offload the existing LTE technology and decrease a network overload by supporting these types of devices which need only small amounts of data, not delay-sensitive and almost stationary.
NB-IoT Standard Requirement
- Decrease the signaling overhead, especially over the air interface.
- Suitable security to the complete system including the core network.
- Improve battery life.
- Support of IP and non-IP data.
- Support of SMS as a deployment option.
So to meet the above-mentioned requirements, many basic and advanced LTE features of LTE Release 8/9 are not supported in like Lack of UEs Handover in the connected mode, Carrier Aggregation, and Dual mode. This is because that NB-IoT is not used for delay-sensitive data packets and consequently, all services requiring a guaranteed bit rate are not offered in NB-IoT.
NB-IoT Frequency Bands
3GPP defined a set of frequency bands for which NB-IoT can be used. 3GPP TS 36.101 from release 13 provides the following bands: 1,2,3,5,8,12,13,17,18,19,20,26,28,66 and Release 14 added the bands: 11, 25, 31 and 70. Regarding Release 15, It added further bands: 4,14 and 71.
The details of Release 13 bands are as below :
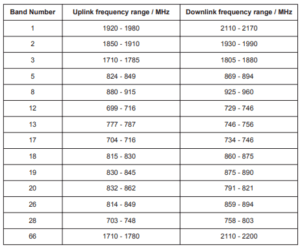
NB-IoT Release 13 Frequency Bands
The interesting note here that most frequencies are in the lower range of the existing LTE bands to can operate in difficult radio conditions.
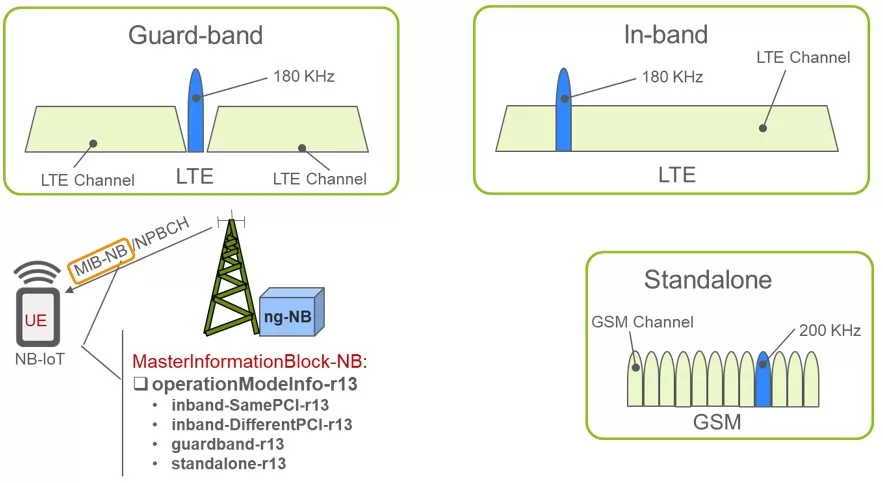
NB-IoT Mode Flexibility
As the spectrum is a scarce resource, NB-IoT needs to use as little as possible (180KHz) and also coexist with already current radio technologies. To achieve this, NB-IoT offers 3 different options:
- Stand-Alone: Use one of the current GSM frequencies. So still there’s still a guard interval of 10 KHz remain remaining on spectrum both sides.
- Guard-Band: Use free resource block within an LTE guard band.
- In-Band: Use a resource block within an LTE frequency band.
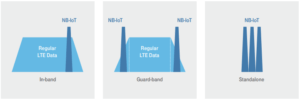
NB-IoT Mode Flexibility
Also for Release 13, FDD half duplex is chosen as the duplex mode and this means that UL and DL are separated in frequency and the UE either transmits or receives, however not simultaneously.
NB-IoT Use Cases
NB-IoT provides high coverage with low cost and this will be appropriate for different use cases as below:
- Smart Metering, Utility sector applications like heating, water or electricity are ideal for NB-IoT due to some reasons: a high number of devices, a small amount of data and they’re located in buildings.

Smart Meter
- Smart Waste Management, as the majority of the cities, provide waste disposal on a fixed schedule. The intelligent wase management now targets emptying garbage bins only whenever they’re full with the help of the sensors that send recorded data via NB-IoT to a cloud server for data analysis and also to calculate the most effective route.
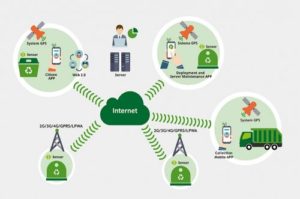
Manhattan, United States – MarketersMediaNB-IO
NB-IoT Advantages
- It uses the mobile network, so it provides better flexibility, QoS and security versus the unlicensed Low Power Wide Area technologies like LoRa and Sigfox.
- It extends the coverage and distance as it can support 20 dB better compare to the GSM/GPRS network and covers around 20 Km from the cell.
- It can co-exist with the other legacy cellular systems like LTE.
- It provides very low power consumption tends to 10 years.
NB-IoT Challenges
- It suitable only for stationary devices and it offers a lower data rate of around 250 Kbps for Download and 20 Kbps for Upload.
- It doesn’t support Voice or Roaming.
- In poor coverage areas, It’s needed to send data multiple times to make sure the data reception and this leads to high power consumption due to inappropriate network implementation.
Resources
- 3GPP.
- GSMA.
- Rohde & Schwarz